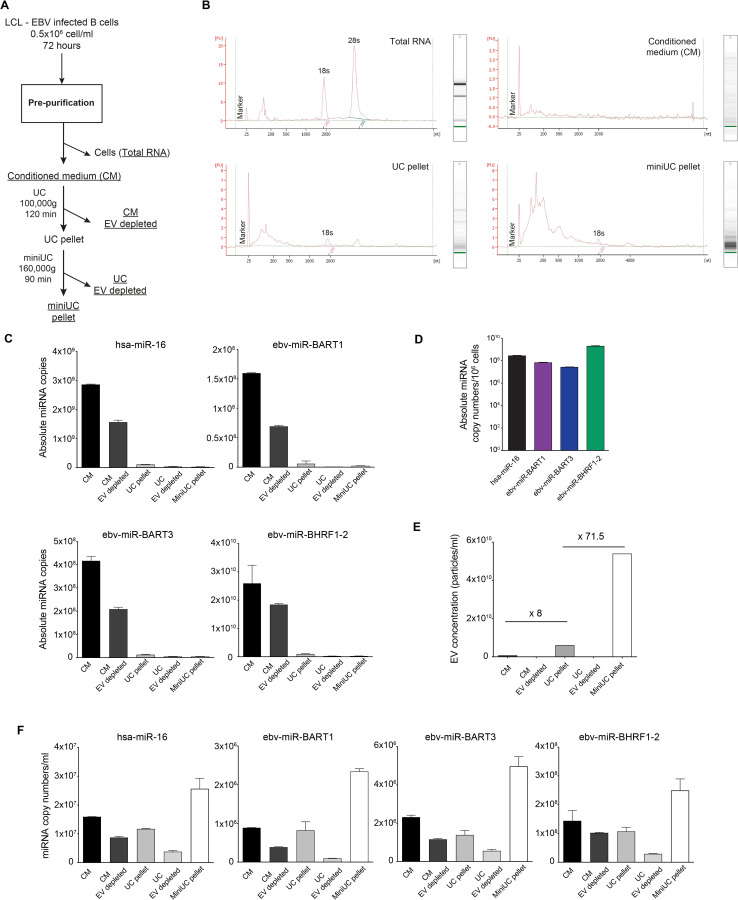
Fig 2. microRNAs quantitation during different steps of EV purification.
(A) Schematic overview of EV sample collection and purification. After 72 h of LCL cell culture, we collected (i) the cell supernatant (‘conditioned medium’; 180 ml), (ii) the pellet after ultracentrifugation (‘UC pellet’; 9 ml), (iii) the supernatant after ultracentrifugation (‘conditioned medium EV depleted’ (180 ml), (iv) the pellet after the second ultracentrifugation step (‘miniUC pellet’; 1 ml), and (v) the remaining supernatant (‘UC EV depleted’; 9 ml). RNA was extracted from 200 μl of each sample. As a control ‘total RNA’ from 1×106 LCLs was prepared. (B) Electropherograms after Bioanalyzer analysis of four samples are shown with their extinction profiles. (C) Using a Taqman stem loop RT-qPCR protocol, absolute copy numbers of four miRNAs were determined in different steps of EV purification as shown in panel A. For each of the four individual miRNA, a regression function with a synthetic miRNA oligonucleotide was generated by RT-qPCR for its absolute quantification. The different sample volumes were considered, according to the legend of panel A. (D) Absolute copy numbers of a human and three viral miRNAs in 106 EBV-infected B cells (LCLs) are provided. (E) Concentrations of EV particles contained in different samples as indicated were measured by NTA. Numbers indicate fold-changes between ‘conditioned medium’ and ‘UC pellet’ (×8) and ‘conditioned medium’ and ‘miniUC pellet’ (×71.5) as explained in panel A. (F) Concentrations of four individual miRNAs (three viral miRNAs and a representative cellular miRNA) are shown in the different steps of EV purification as illustrated in panel A. Error bars in panels C–F indicate mean and SD of triplicates. Data obtained from one experiment of two independent experiments are shown.