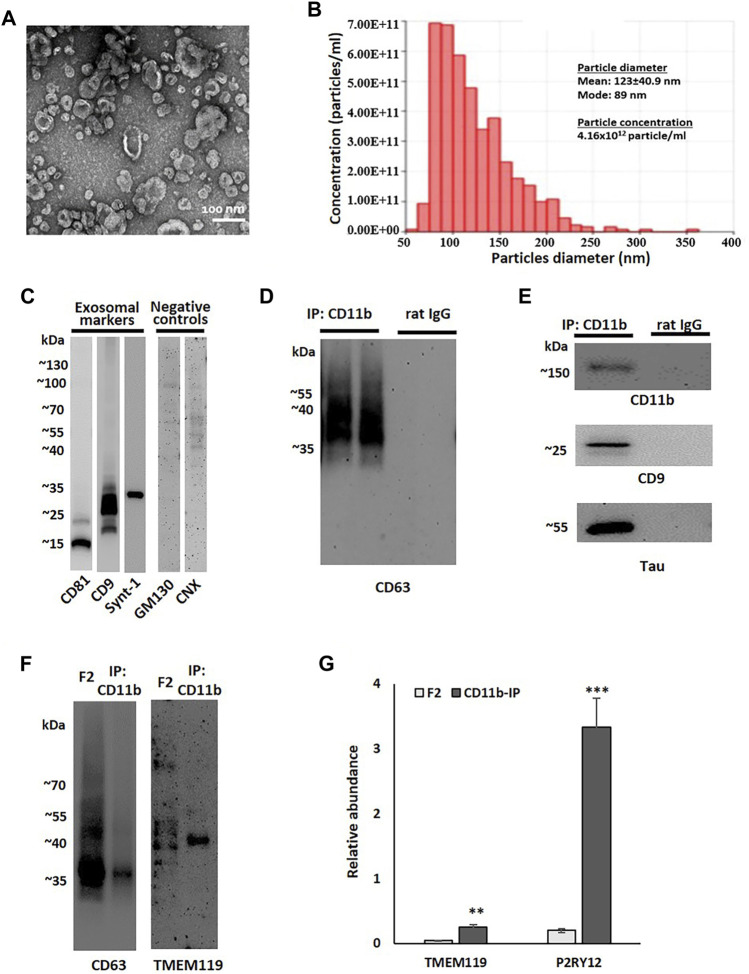
FIGURE 1.
Small EV fraction characterization and microglial EV purification. (A) Representative transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image of small EV fraction (F2) isolated from the human parietal cortex. (B) Tunable resistive pulse sensing (TRPS) analysis of the F2 fraction isolated from the human parietal cortex. (C) A representative image of immunoblot analysis of an F2 fraction using antibodies against exosomal markers (CD9, CD81, and syntenin-1) and negative control markers (GM130 and calnexin, CNX). (D) A representative image of immunoblot analysis of two immunoprecipitation (IP) samples pull-down either with antibodies against microglial marker CD11b or with corresponding isotype control antibodies (rat IgG2b). Membrane was probed with the exosomal marker CD63. (E) Immunoblotting of CD11b-IP samples and isotype control samples probed with antibodies against a microglial marker (CD11b), an exosomal marker (CD9), and tau. (F) Immunoblotting of the F2 fraction isolated from the human parietal cortex and corresponded CD11b-IP fraction with antibodies against the exosomal marker CD63 and the microglial marker TMEM119. The sample volume was equal between CD63 and TMEM119 immunoblots. (G) Relative abundances of microglial markers, TMEM119 and P2RY12, in F2 (n = 6) and CD11b-IP samples (n = 7) as indicated by LC-MS/MS (**p < 0.001; ***p < 0.0001).