Fig. 2.
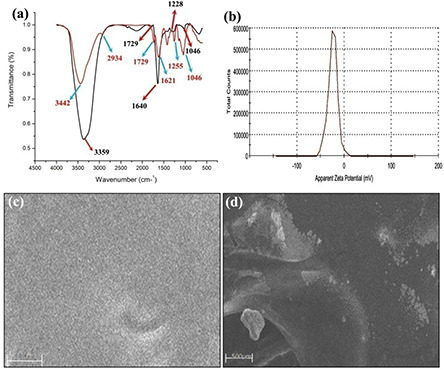
FTIR analysis
(a) Native soluble GK: and after nanoparticle formation indicating the involvement of various functional groups. Functional groups such as hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxylate, acetyl and C–O were identified to be involved in the nanoparticle formation. (b) Zeta potential of GK‐(Ag–Au) NP, indicating the stability of GK‐(Ag–Au) NP. SEM micrographs of GK (c) soluble gum (d) after nanoparticle formation. GK appeared in the form of a homogenous layer with uniform distribution of the polymer while in the case of GK‐(Ag–Au) NP, it showed uniform distribution of nanoparticles
