FIGURE 3.
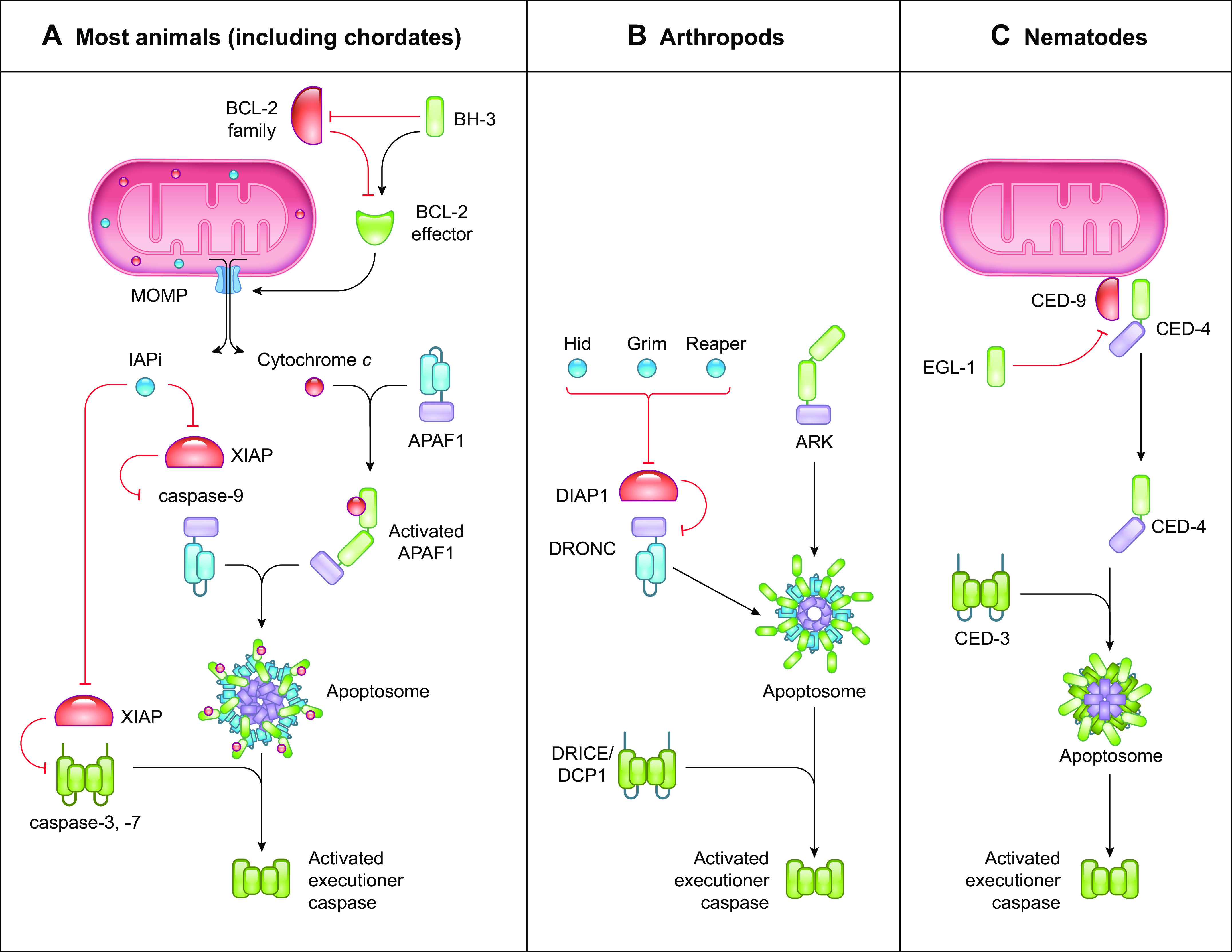
The caspase-9 pathway of apoptosis. Comparison between the caspase-9 pathway of apoptosis in most animals, arthropods, and nematodes. A: in most animals, the caspase-9 pathway of apoptosis is mediated by the BCL-2 effector proteins BAX and BAK to induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). Activation of BCL-2 effector proteins is regulated by the balance between proapoptotic and antiapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. MOMP releases cytochrome c and inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) inhibitors (IAPi) into the cytosol, where cytochrome c binds and activates Apoptotic Protease Activating Factor 1 (APAF-1) to recruit the initiator caspase-9, forming the apoptosome. Activated caspase-9 cleaves and activates the executioner caspases-3 and -7 to mediate apoptosis. IAPi released by MOMP block the suppressive effects of the caspase inhibitor X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP), allowing the caspases to function. B: in arthropods, the APAF-1 homolog ARK is constitutively active. The IAP inhibitors Hid, Grim, and Reaper inhibit DIAP1 to release the initiator caspase DRONC to form the apoptosome with ARK. Activated DRONC cleaves and activates the executioner caspases DRICE and DCP1 to induce apoptosis. C: in nematodes, the APAF-1 homolog CED-4 is suppressed by the anti-apoptotic protein CED-9. Binding of the BH-3-only protein EGL-1 to CED-9 releases CED-4 to form the apoptosome with the executioner caspase CED-3, resulting in CED-3 activation and apoptosis.
