Figure 2.
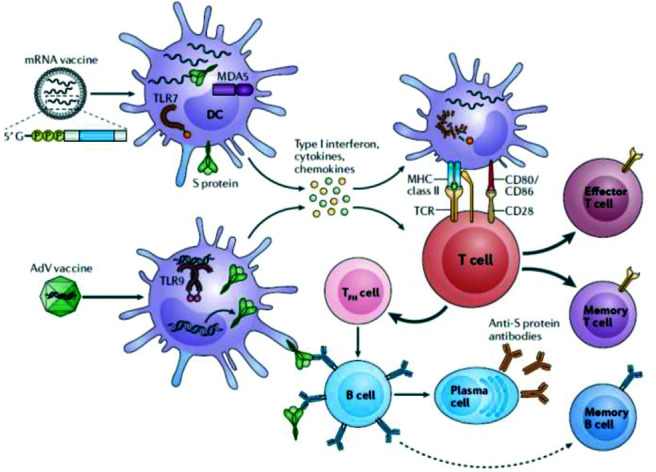
How mRNA and AdV vector vaccines elicit immunity to SARS-CoV-2. The two vaccine formulations, i.e., mRNA vaccine(s) and the AdV vectorized vaccine gain entry into DCs, which results in the production of high levels of S protein. In addition, innate sensors are triggered by the intrinsic adjuvant activity of the vaccines, which results in production of type I interferon and multiple pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. RNA sensors, such as TLR7 and MDAS are triggered by the mRNA vaccines, and TLR9 is the major double-stranded DNA sensor for the AdV vaccine. The resultant activated DCs present antigen and costimulatory molecules to S protein–specific naive T cells, which become activated and differentiated into T cytotoxic effector cells or T-helper lymphocytes. TFH cells help S protein–specific B cells to differentiate into antibody-secreting plasma cells and promote the production of high-affinity anti–S protein antibodies. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 6. mRNA = Messenger RNA; AdV = adenovirus; SARS-CoV-2 = severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; DC = dendritic cell; S = spike; TLR = Toll-like receptor; MDAS = melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5; TFH = T follicular helper.
