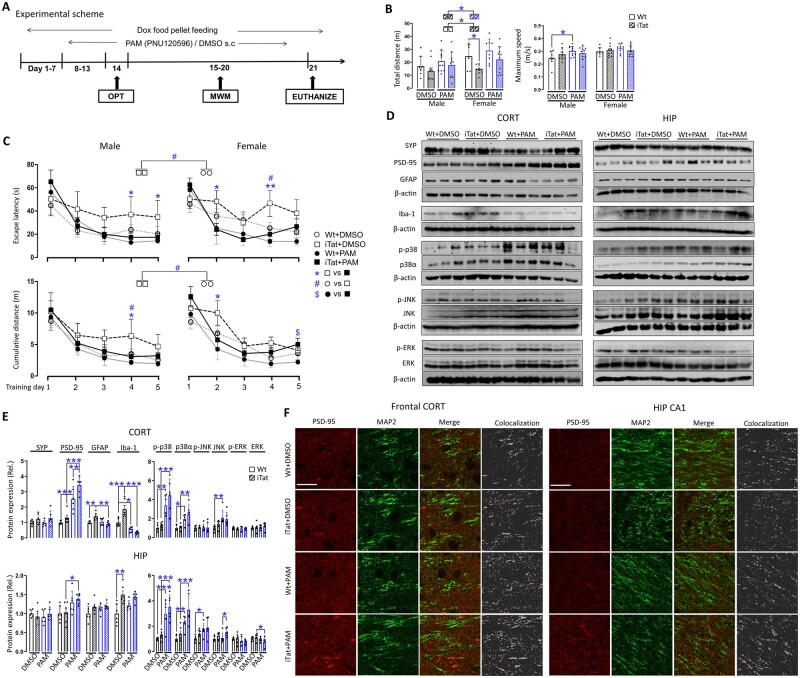
Figure 1.
Effects of PAM on HIV-1 Tat-induced behavioural impairments and neuropathologies. (A) Wild-type (Wt) or iTat mice 3–4 months of age were fed with doxycycline (Dox)-containing food pellets and injected subcutaneously (s.c.) with PAM PNU-125096 (15 mg/kg/day) or its solvent DMSO control, and grouped by sex (n = 6–11/group). The mice were subject to an open field test (B) and Morris Water Maze test (training stage, C), and the behavioural indices were determined by the ANY-maze software. During the behavioural tests, doxycycline-containing food pellet feeding continued ad libitum, PNU-125096 was administrated within 5 h following each behavioural test. (D) On Day 21, 1 day after the last behavioural test, all mice were euthanized, cortex (CORT) and hippocampus (HIP) were dissected out to determine expression of synaptophysin (SYP), PSD-95, GFAP and Iba-1, and total and phosphorylated p38, JNK and ERK by western blotting. (E) Protein expression was quantified by densitometry and normalized to the loading control β-actin and calculated using Wt+DMSO as a reference, which was set at 1 (n = 6/group, three males and three females). (F) Immunofluorescent staining was performed for PSD-95 and MAP2 expression. Scale bars = 20 µm. Subregions in frontal cortex and hippocampus CA1 were chosen as representative region for the cortex and hippocampus, respectively. P < 0.05 was considered significant and is indicated with asterisk, number symbol or dollar sign for comparisons among different groups; **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 were both considered highly significant and are indicated with asterisks.