Figure 1. The IGF-Trap preferentially inhibits the growth of liver metastases in an orthotopic PDAC model.
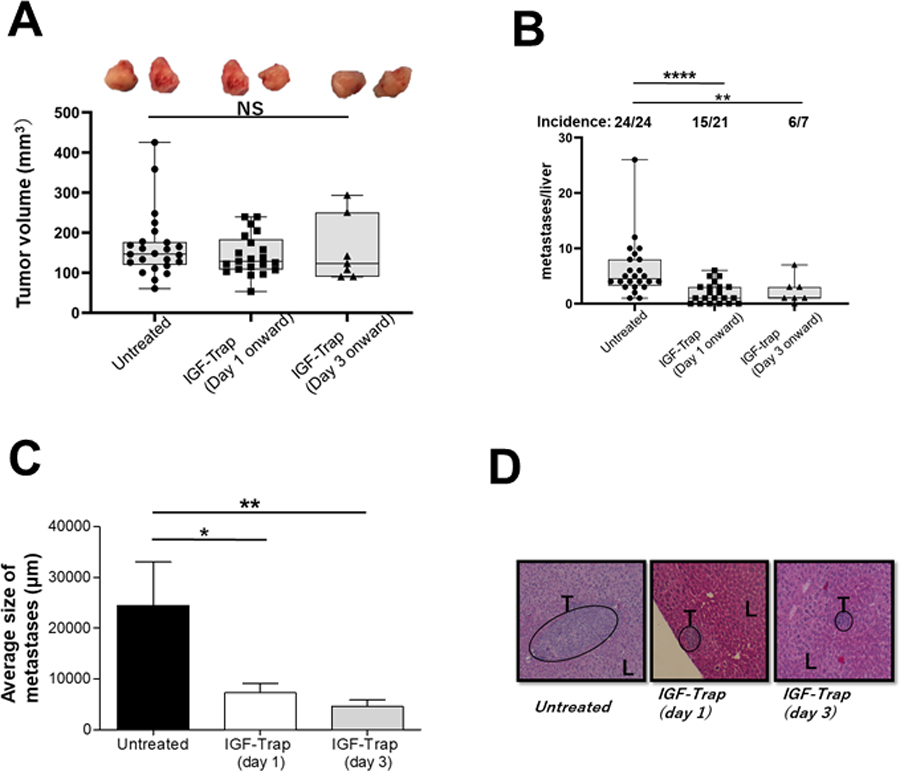
LMP cells (5x105 in Matrigel) were implanted in the pancreas of immunocompetent, histocompatible B6/129F1 (B129) male mice. Treatment with 5mg/kg IGF-Trap 3.3 (or PBS) was initiated 1 (IGF-Trap (Day1)) or 3 (IGF-Trap (Day 3)) days later and continued on alternate days for a total of 5 injections per mouse. Animals were euthanized 3 weeks post tumor implantation, local pancreatic tumors measured and visible metastases on the surface of the liver enumerated. Results are based on pooled data from 4 independent experiments in which each treatment group consisted of 5–7 mice. Shown in (A) are the numbers of metastases per liver and (on top) the incidence of hepatic metastases per group. Shown in (B) are the average sizes of the metastases expressed as means (±SD) in each group and in (C) representative H&E stained PPFE sections of livers from each of the treatment groups. Shown in (D) are the volumes of individual local pancreatic tumors of the same mice calculated using the formula 1/2(length x width2) with 2 representative tumors from each of the treatment groups shown on top. Box and whiskers graphs: the box extends from the 25th to 75th percentiles, the middle line denotes de median and the whiskers extends from the minimum to the maximum value. *p ≤ 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001; NS-not significant.
