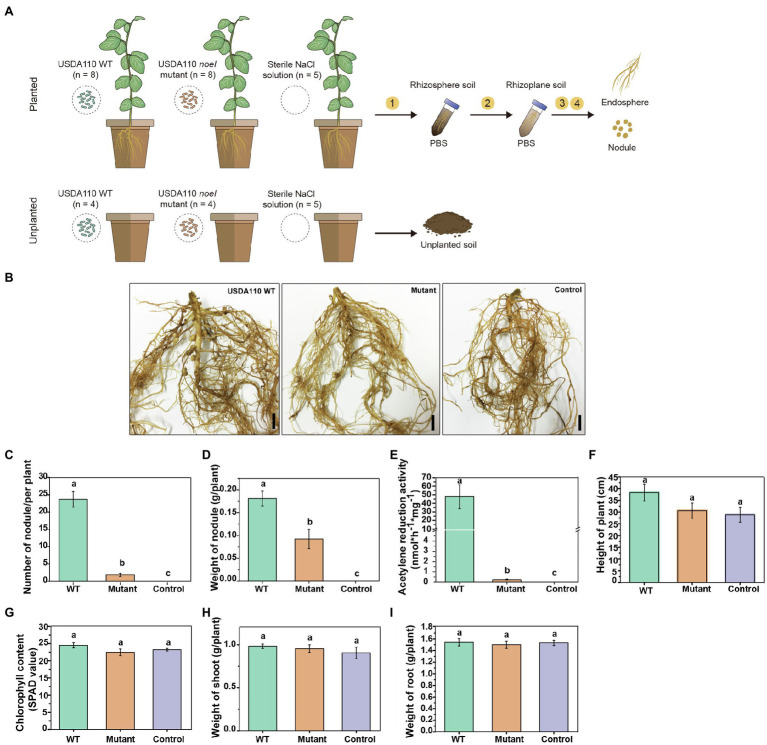
Figure 1.
The experimental design and symbiotic phenotypes of soybean inoculated with rhizobia. (A) Soybean plants (Glycine max C08) were inoculated with Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens USDA 110 WT or noeI mutant. Sterile 0.8% NaCl solution was used as control. The rhizosphere soil, rhizoplane soil, endosphere, and nodules were sampled 45days post-inoculation (dpi). In addition, unplanted soil samples treated with the same treatments were collected at 45 dpi. ① Rhizosphere soil samples were collected by vortexed shaking and washing in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) buffer, ② rhizoplane soil samples were collected from sonicating and washing, ③ endosphere samples were obtained by surface-sterilizing, and ④ nodules were collected from the cleaned roots. (B) Images depicting the root system of soybean plants inoculated with the USDA 110 WT or the noeI mutant or the control solution (scale bars: 1cm); Scored nodulation phenotypes included (C) number of nodules per plant, (D) nodule weight, (E) nodule nitrogenase activity, (F) height of plant, (G) leaf chlorophyll content (SPAD), (H) dry weight of shoots and, (I) dry weight of roots. Means and standard errors are based on 16 scored plants; different letters indicate significant differences among treatments [Least Significant Difference (LSD) test, p<0.05].