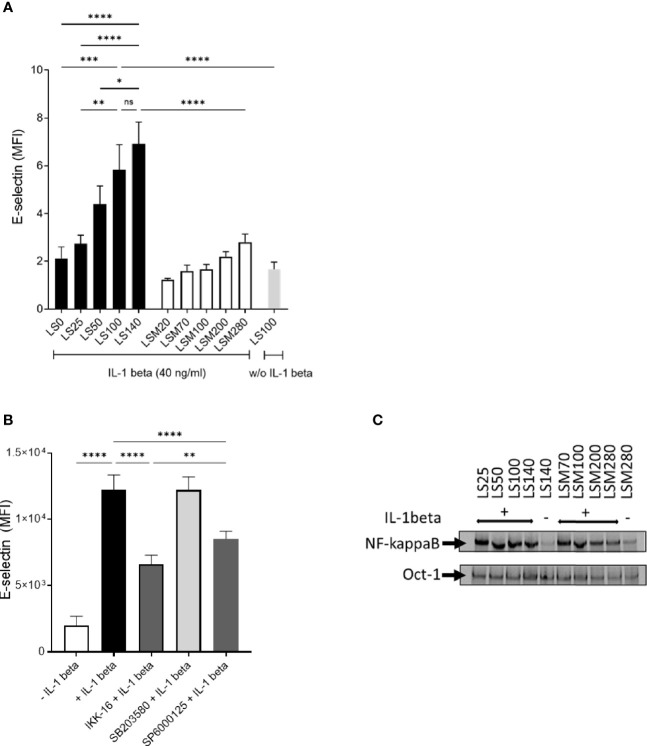
Figure 2.
Lowering NaCl concentration in cell culture medium inhibits cytokine-induced E-selectin expression on endothelial cells in a NF-kappaB-independent manner. (A) Murine mesenteric lymph node–derived endothelioma cells (mlEnds) were cultured in solutions under respective conditions for 24 h before E-selectin was induced by IL-1 beta (40 ng/ml) for 4 h. E-selectin expression on mlEND cell surface was analyzed by flow cytometry and expressed as mean fluorescence intensities (MFI). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01,***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns = non-significant. p-values were calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. All data were expressed as ± SEM from three independent experiments with technical duplicates. (B) mlENDs were pre-treated with an NF-kappaB inhibitor (IKK16;500 nM), a p38 inhibitor (SB203085;10 µM), and a JNK inhibitor (SP6000125; 10 µM) for 1 h before E-selectin expression was induced by IL-1 beta. MFIs of E-selectin are shown. ****p < 0.0001. p-values were calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. All data were expressed as ± SEM from three independent experiments with technical duplicates. (C) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) to analyze NF-kappaB nuclear DNA-binding activity under NaCl restriction. mlENDs were cultured in respective media (LS25, LS50, LS100, LS140, LSM20, LSM70, LSM200, and LSM280) and incubated for 1 h with 40 ng/ml IL-1 beta. Nuclear extracts were applied to NF-kappaB and Oct-1 EMSA. Oct-1 was used as loading control. One representative independent experiment out of four experiments is shown.