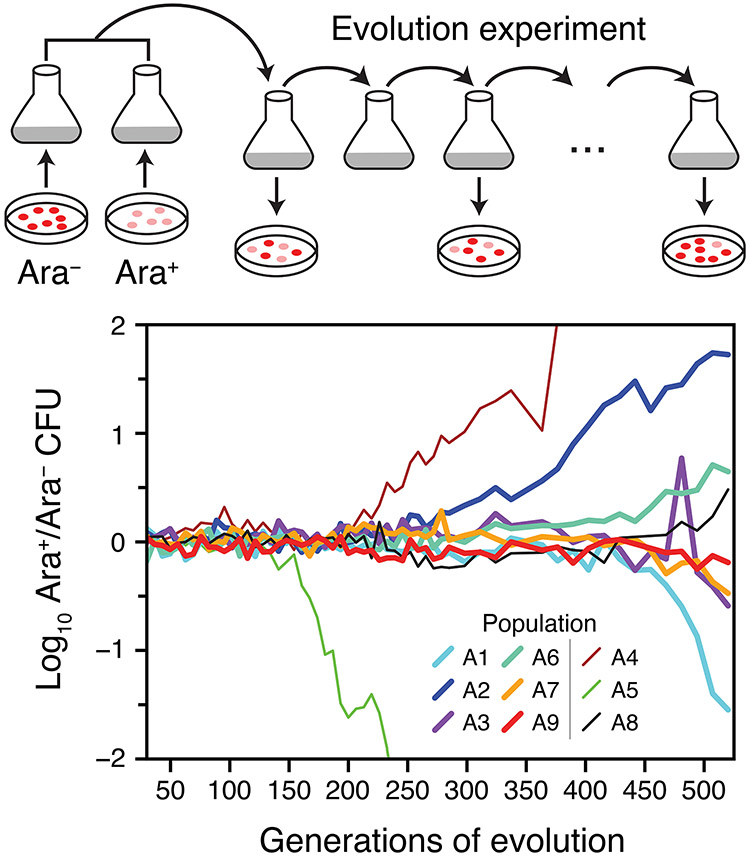
Figure 1. Replaying the first selective sweep of a long-term evolution experiment.
Nine E. coli populations were initiated from equal mixtures of two variants of the ancestral strain that differ in a neutral genetic marker for arabinose utilization (Ara). We observed the evolutionary dynamics of these populations over 500 generations of regrowth from 75 daily 1:100 serial transfers by periodically plating dilutions of each population on indicator agar. Each ancestral strain subpopulation was derived from a single colony isolate that experienced 30 generations of growth before it was combined with the opposite type to initiate the serial transfers. The ratio of Ara+ cells (pink colonies) to Ara− cells (red colonies) diverges from 1:1 when descendants of one ancestor type accumulate enough of a fitness advantage due to de novo beneficial mutations that they take over. We focused further analysis on six of the nine populations (thick lines).