Figure 19.
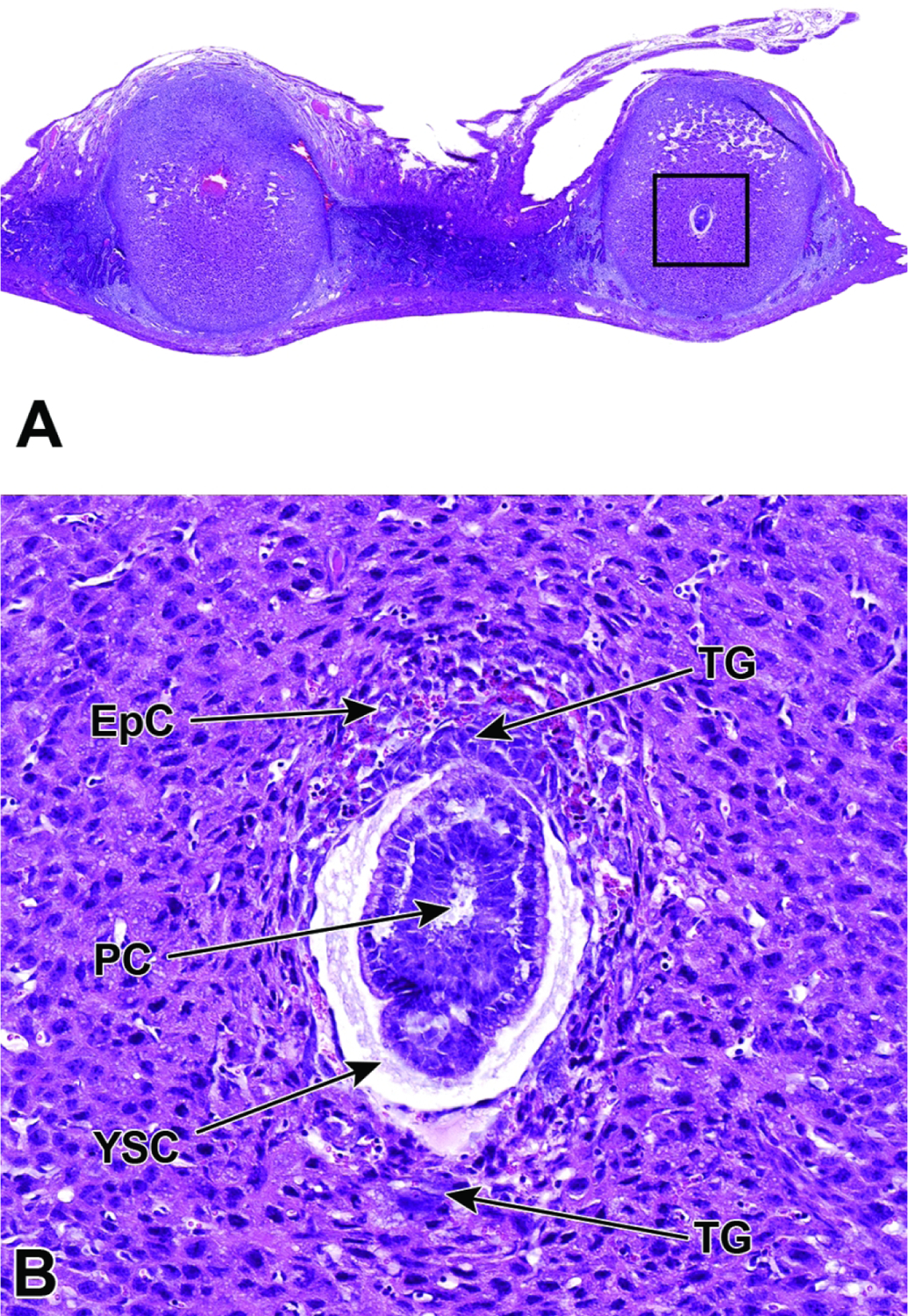
Representative images of a uterine horn and two implantation sites at E6.5. Figure A: At this stage the interaction between maternal decidua and embryonic trophoblast is the main source of embryonic nutrition. Figure B: Higher magnification of this implantation site (boxed region in Figure A) shows the ectoplacental cone (EpC) has formed and contains maternal blood, while trophoblast giant (TG) cells encompass the embryo. As the ectoplacental cone develops, the proamniotic cavity (PC) begins to form in tandem with initiation of gastrulation (formation of the three main embryonic germ layers – the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm). The yolk sac cavity (YSC) is clearly seen at this stage of development. The yolk sac cavity is formed as the visceral yolk sac and parietal yolk sac line the embryo and the inner layer of blastocyst wall, respectively.
