Figure 3.
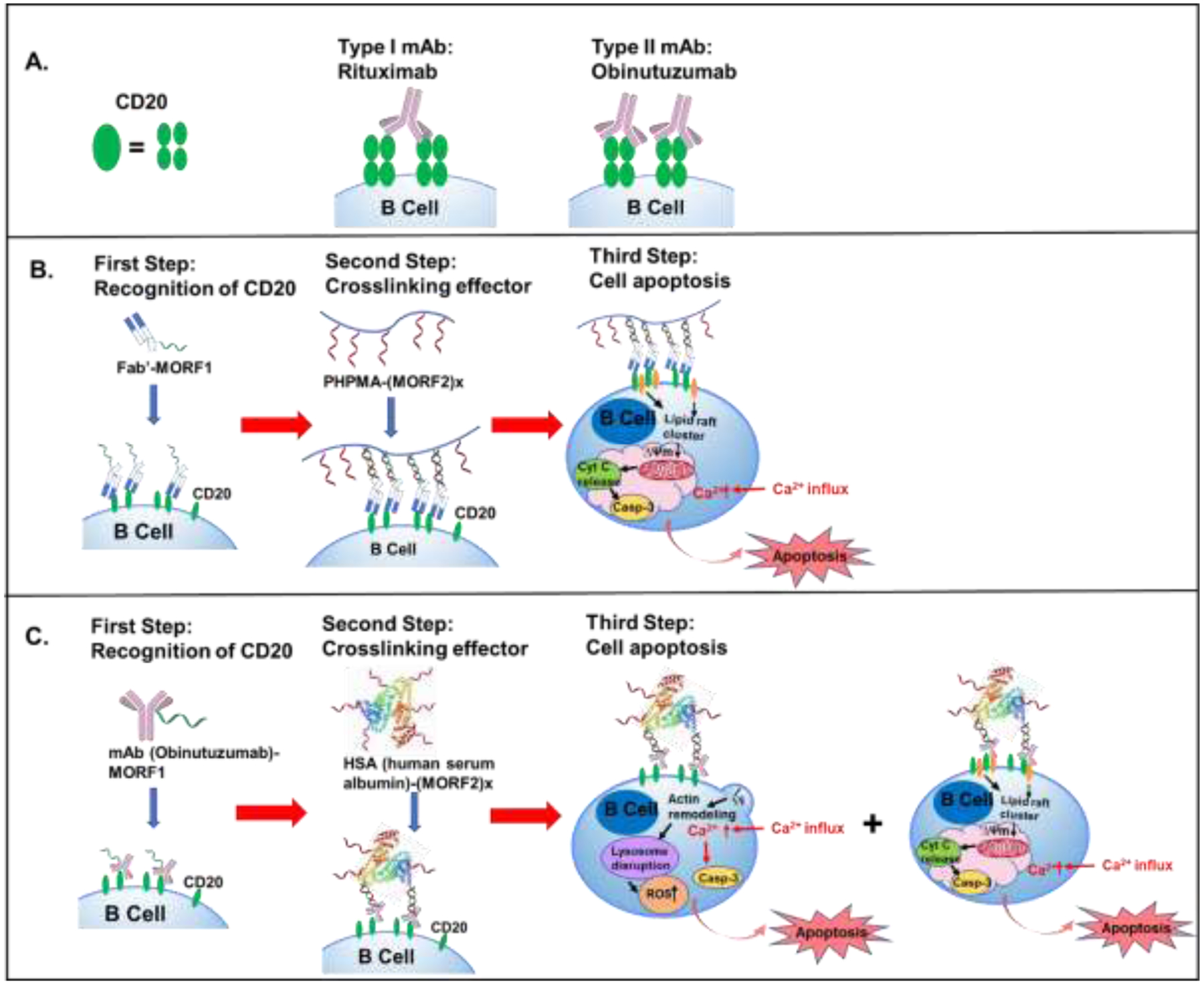
A. CD20 receptor is composed as a tetramer. Type I antibody like rituximab (RTX) binds to two different tetramers (inter-tetramer binding), inducing CD20 redistribution in lipid rafts. Type II antibody like obinutuzumab (OBN) binds within the same tetramer (intra-tetramer binding), which doesn’t cause CD20 redistribution. B. Treatment of Fab’-MORF1 followed by P-(MORF2)x causes raarangement of CD20 complexes in lipid rafts, leading to calcium influx and caspase activation and finally cell apoptosis. C. Second generation of DFMT: binding to CD20 of OBN-MORF1 conjugate initiates actin remodeling, thus trigger lysosome disruption and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, resulting in onset of Type II apoptosis. In addition, crosslinking of the CD20-OBN-MORF1 complex with HSA-(MORF2)X leads to clustering the CD20 complexes in lipid rafts thus triggering Type I apoptotic effects.
