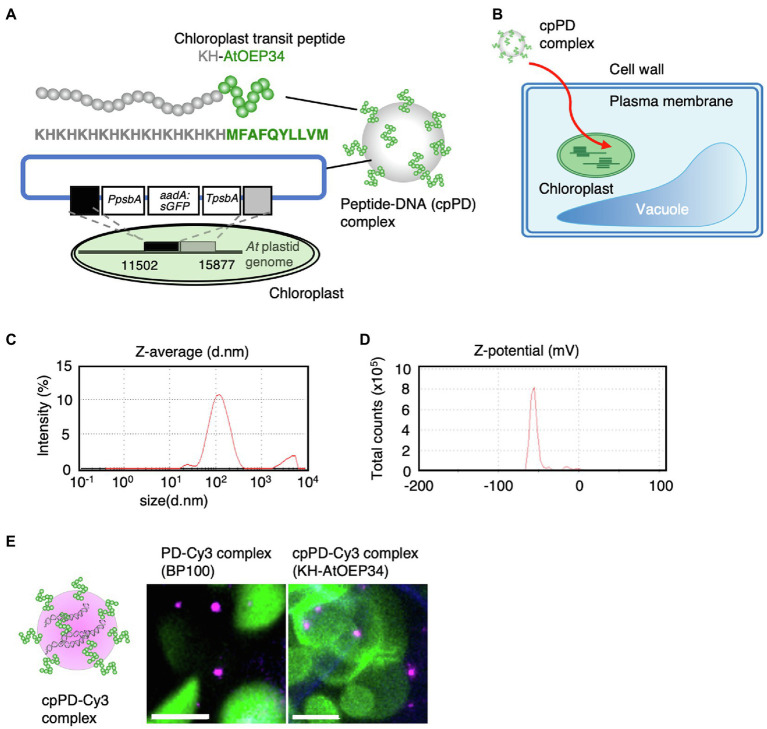
Figure 1.
Characterization of the peptide–DNA complex used in this study. (A) Schematic diagram of the peptide–DNA complex KH-AtOEP34–pDNA (cpPD complex) used in this study. The protein sequence of the KH-AtOEP34 peptide is shown in gray (KH) or green (AtOEP34). Plasmid DNA used for integrating exogenous DNA into Arabidopsis thaliana (At) plastid genome is shown below. Each box represents DNA fragments, PpsbA, promoter of psbA; aadA-sGFP, a sequence coding aminoglycoside adenyltransferase (aadA) fused to sGFP; TpsbA, terminator sequence of psbA; black and gray boxes; sequence used for integration into chloroplast genome. (B) Schematic diagram of the path of cpPD complexes from the extracellular space of a leaf cell to the chloroplast stroma. (C,D) Z-average (C) and Z-potential (D) of cpPD complexes in solution. (E) Left, schematic diagram of the KH-AtOEP34–pDNA complex labeled with Cy3 (cpPD-Cy3 complex). Right, representative images of PD-Cy3 complexes (BP100) and cpPD-Cy3 complexes in leaf mesophyll cells. Scale bars denote 10μm.