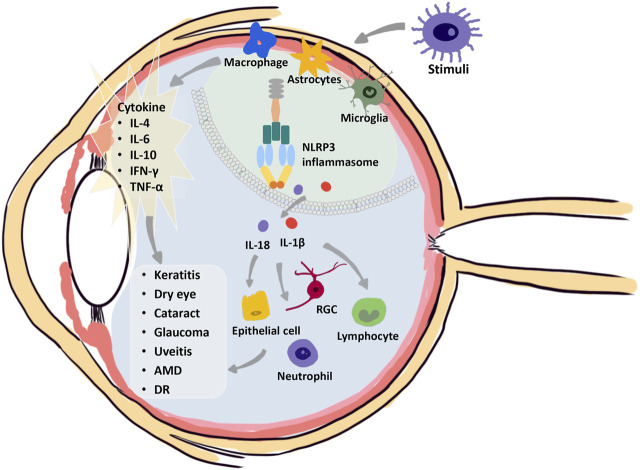
FIGURE 3.
Crucial role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the pathogenesis of eye diseases. The NLRP3 inflammasome mediates eye inflammation occurrence under various stimuli, such as bacterial and viral infections, desiccating stress, autoimmune factors, drusen, and complement proteins. Activation of immune cells results in a cascade of massive inflammatory cytokines, including IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IFN-γ, and TNF-α. Meanwhile, NLRP3 inflammasome activation occurs in activated macrophages, astrocytes, and microglia, which drives the secretion of IL-1β and IL-18 to recruit inflammatory cells and induce the damage or cell death of different cells. Multiple damage factors induce various injuries in the different ocular tissues, leading to keratitis, dry eye, cataracts, glaucoma, uveitis, age-related macular degeneration, or diabetic retinopathy.