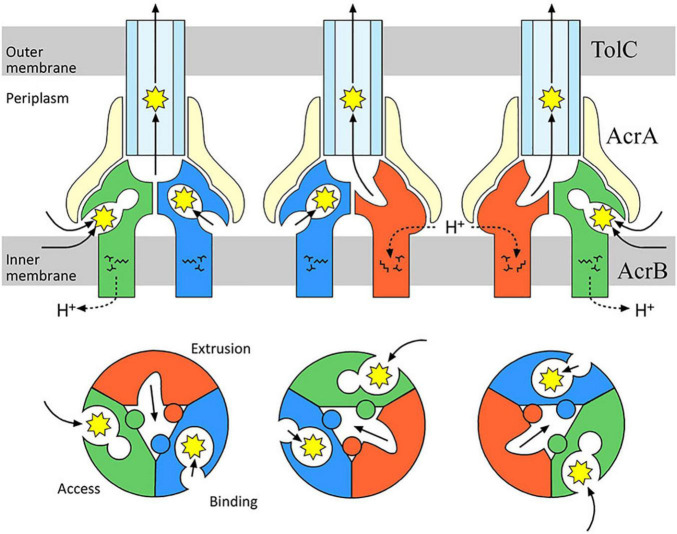
FIGURE 10.
Drug transport via the AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux system. AcrB facilitates the proton motive force as its energy source to extrude drugs from the periplasm or inner membrane to the outside of the cell. During drug-transport, each monomer of the AcrB trimer has a different structure. Drugs are transported in sequence from the Access to the Binding monomer, and then to the Extrusion monomer. We found a drug-recognition pocket near the entrance called the Proximal Binding Pocket (PBP, expanded in the Access monomer), and a Distal Binding Pocket (DBP) near the exit (expanded in the Binding monomer). Erythromycin (molecular weight: 734 g mol–1) and rifampicin (molecular weight: 823 g mol–1), two drugs with a relatively large molecular weights, temporarily bind to the PBP, then they are sent to the DBP via a peristaltic pump mechanism (Nakashima et al., 2011).