Figure 2.
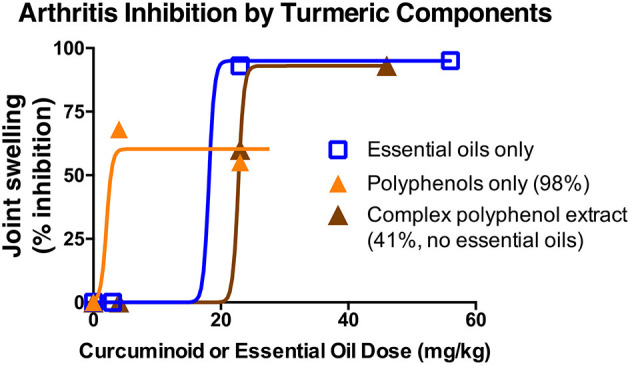
Differential anti-arthritic effects of components extracted from turmeric rhizome in a pre-clinical arthritis model. The anti-arthritic effects of turmeric extracts of different chemical composition were assessed using an ip dosing strategy given reports of altered oral curcuminoid bioavailability when combined with essential oils. Each of turmeric's secondary metabolites [curcuminoids (orange triangles) and essential oils (blue squares)] had significant anti-arthritic effects when administered separately. Interestingly, differential effects were noted for a chemically complex curcuminoid extract (brown triangles) devoid of essential oils but containing polar compounds, such as polysaccharides. Anti-arthritic curcuminoid efficacy was confirmed with oral dosing [50% inhibition; human equivalent dose (HED) of 1 g/d], while protection from oral essential oils was much reduced (20%; HED of 5 g/d) (13).
