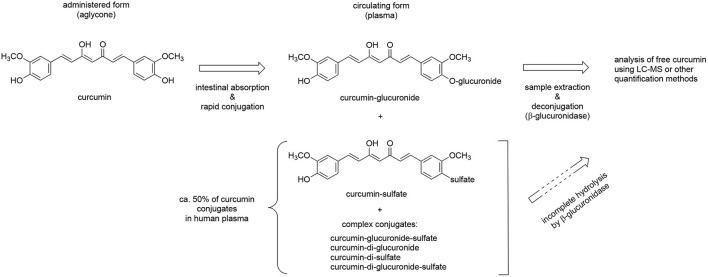
Figure 3.
Metabolic conjugation of curcumin and deconjugation for quantitative analysis. Curcumin is consumed in its free (aglycone) form and undergoes rapid phase II conjugation following intestinal absorption. The glucuronide conjugate accounts for about half of the circulating conjugates while sulfate and other, more complex conjugates account for the rest. Free curcumin is low or undetectable in plasma samples. For quantification plasma samples are often deconjugated using β-glucuronidase but this achieves only incomplete hydrolysis of sulfate and complex conjugates; more complete hydrolysis of all conjugates can be achieved using sulfatase. Direct analysis of conjugates is preferred but hampered by the large number of conjugates, lack of standards, and technical challenges. Reduction of the aliphatic double bonds, a significant route of metabolism in vivo, and other metabolic events are not illustrated.