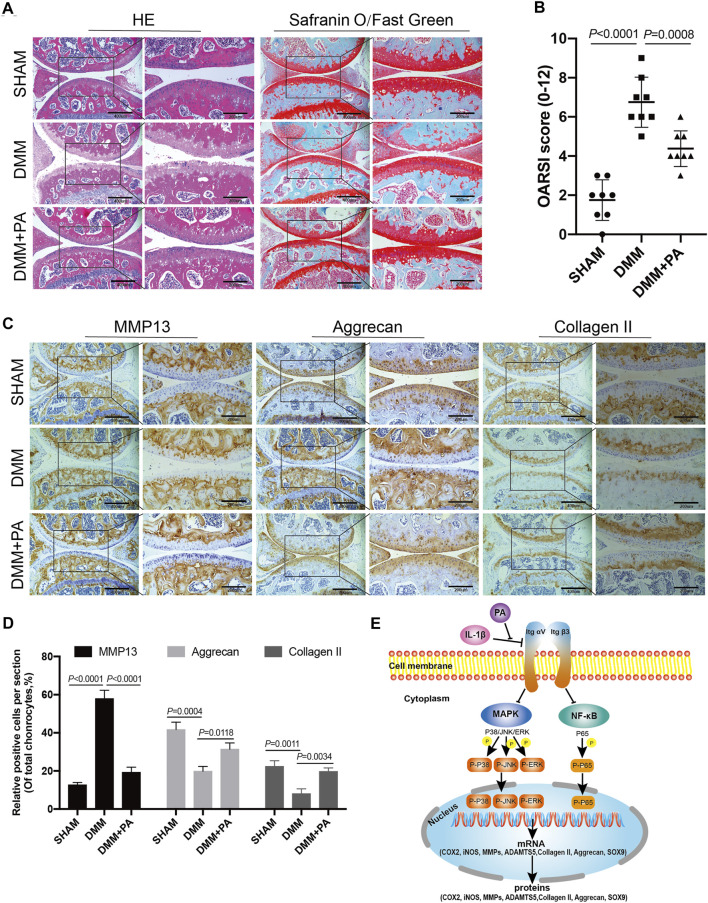
FIGURE 8.
PA attenuated cartilage destruction in the in vivo mouse OA model. (A) HE, Safranin O, and Fast Green staining and (B) OARSI scores of mice knee joints from the sham, DMM, and DMM + PA groups at 8 weeks after the corresponding treatment (scale bars, 200 and 400 μm). (C) Immunohistochemistry staining and (D) quantification of the expression of MMP13, aggrecan, collagen II were measured among the three groups (scale bars 200 and 400 μm). Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 6). The exact p value was marked in the corresponding figure and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. (E) The potential molecular mechanism of PA’s chondroprotective effect. PA could alleviate the inflammatory response and cartilage degradation of IL-1β-induced chondrocytes by inhibting the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways, and the beneficial effect of PA on OA may be mediated through integrin αVβ3.