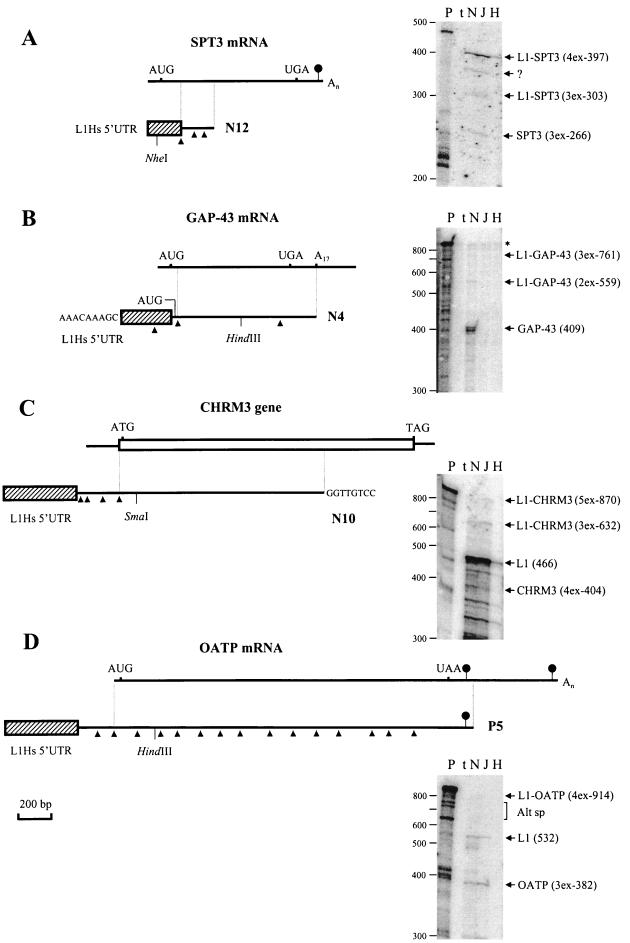
FIG. 3.
Graphical representation and detection in different cell lines of chimeric transcripts generated from the L1Hs ASP. Diagrams show alignments of N12 and SPT3 mRNA (A), N4 and GAP-43 mRNA (B), N10 and CHRM3 gene (C), and P5 and OATP mRNA (D). Chimeric cDNAs and mRNAs are indicated by lines, the CHRM3 gene (mRNA sequence unknown) is shown by an open box, and L1Hs 5′UTR sequences transcribed from the L1Hs ASP and linked to the known mRNA and gene sequences are indicated by hatched boxes. Identical regions between mRNA (gene) and chimeric cDNAs are shown by vertical lines. Introns, determined from the alignment of genomic and cDNA sequences (Table 1), are shown by arrowheads below cDNA structures only for aligned portions and 5′ regions of chimeric cDNAs. Initiator AUG/ATG and stop codons are shown above the lines; polyadenylation signals (not found for the structures of GAP-43 mRNA and CHRM3 gene depicted) are marked by oval arrows. Additional sequences were found at the 5′ end of N4 and 3′ end of N10 cDNAs. Their origin is unclear. Detection of the four chimeric transcripts in different cell lines by using RNase protection (27) is shown at the right. All protected RNAs were analyzed on a 5% denaturing polyacrylamide gel by using the following 32P-labeled probes. (A) A 465-nt riboprobe encompassing 131 nt of the L1Hs 5′UTR, three exons of SPT3 mRNA (85, 87, and 94 nt), and 68 nt of vector sequences was generated from N12, cut with NheI, and transcribed with T7 RNA polymerase. (B) A 829-nt riboprobe encompassing two exons of the L1 5′UTR (150 and 202 nt), 409 nt of 5′ region of the GAP-43 mRNA, and 59 nt of vector sequence was generated from a HindIII deletion subclone of N4, cut with EcoRI, and transcribed with T3 RNA polymerase. (C) A 934-nt riboprobe encompassing 450 nt of the L1 5′UTR plus 16 nt of non-L1 sequence, three exons (63, 103, and 127 nt) and 5′ coding region of the CHMR3 gene (111 nt), and 61 nt of vector sequences was generated from a SmaI deletion subclone of N10, cut with EcoRI, and transcribed with T7 RNA polymerase. (D) A 1,009-nt riboprobe encompassing 429 nt of L1 5′UTR plus 103 nt of non-L1 sequence, 5′ region of OATP mRNA (three exons, 382 nt), and 94 nt of vector sequences was generated from a HindIII deletion subclone of P5, cut with XhoI, and transcribed with T7 RNA polymerase. Restriction enzymes used to make riboprobes and deletion subclones are shown below cDNA structures. Chimeric and alternative mRNAs detected are shown on the right of each panel. For these mRNAs, the number of exons (xex) and their sizes in nucleotides are indicated in parentheses. Protected fragments of N10 and P5 predict three and one additional exons for the 5′ ends of CHMR3 and OATP mRNAs, respectively. Protections with the L1Hs 5′UTR of N10 (C) generate several fragments of <466 nt representing highly homologous transcripts derived other genomic L1Hs. Similar protections for N12 and N4 (fragments <200 and <300, respectively) are not shown (A and B). Traces of the undigested probe (B) are shown by the asterisk. A 32P-labeled 100-bp ladder (BRL) was used as a molecular weight marker. P, uncut probe; t, tRNA. In each experiment, 5 μg of total RNAs from NTera2D1 (N), JEG 3 (J), and HeLa cells (H) were used. Alt sp, possible alternatively spliced products; ?, unknown product.