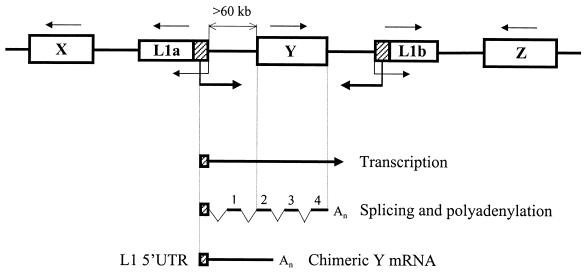
FIG. 9.
Transcriptional regulation by the L1Hs ASP. A fragment of the human genome containing two randomly positioned full-length L1 retrotransposons (L1a and L1b) and genes X, Y, and Z is shown. Direction of transcription for each gene is indicated by a thin arrow above the gene. Transcriptions driven by the L1a and L1b internal promoters (34) and ASPs, driving in opposite direction, are indicated by thin and thick arrows, respectively. Note that gene Y has the same direction of transcription as the L1a ASP but is located >60 kb further downstream. Genes X and Z do not match the L1a ASP orientation. Transcription of gene Y from the L1a ASP can generate a long precursor mRNA which upon splicing and polyadenylation according to the gene Y structure yields a chimeric Y mRNA. This mRNA contains the 5′-terminal L1a 5′UTR in antisense orientation spliced to the exon 1 derived from the intergenic region and exons 2 to 4 of gene Y. The latter structure is depicted at the bottom.