Figure 3.
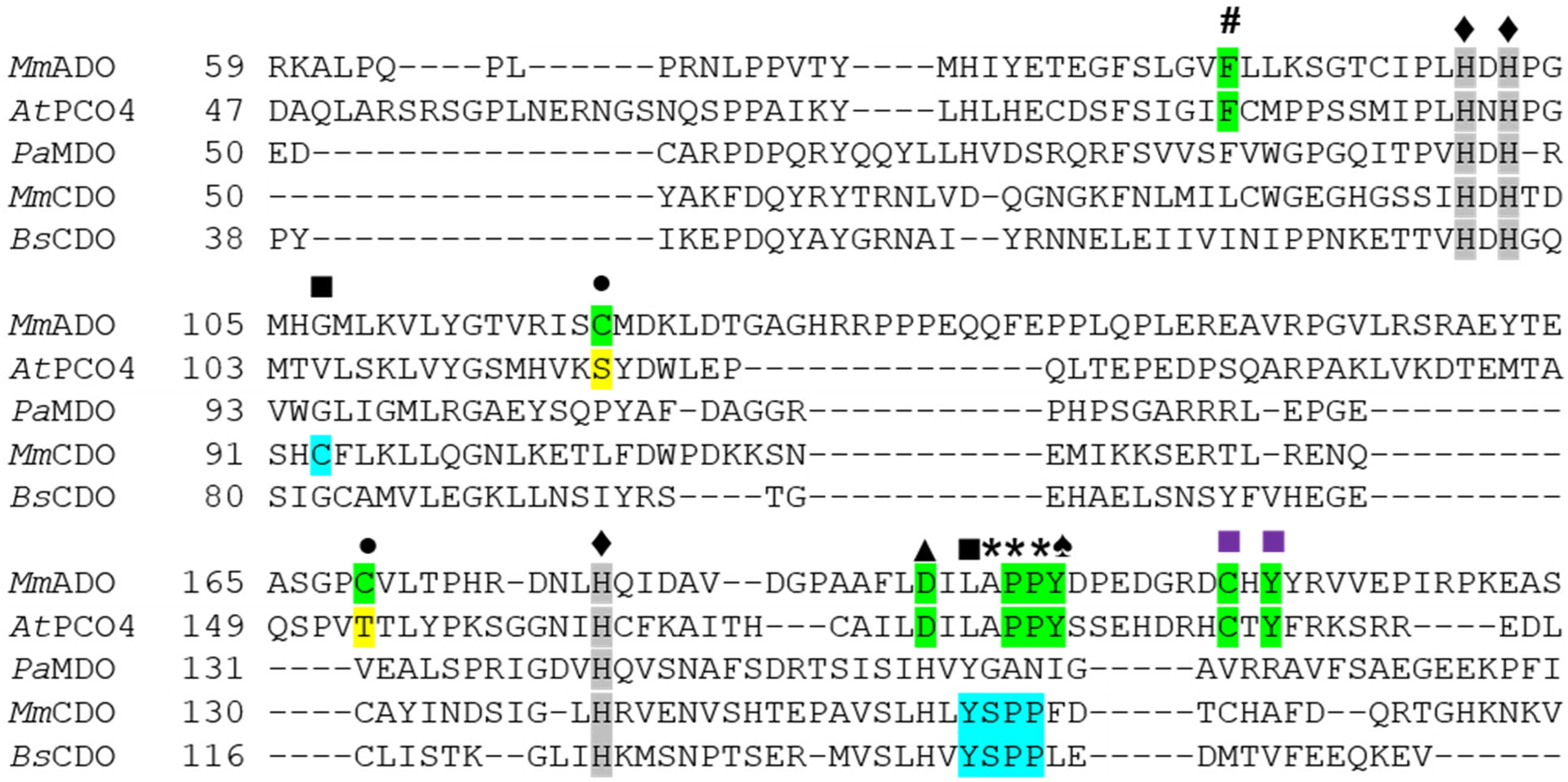
Sequence alignment showing conserved residues within TDOs. The sequences of the PCO4 from Arabidopsis thaliana (AtPCO4), the MDO from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PaMDO), and the CDOs from Mus musculus (MmCDO) and Bacillus subtilis (BsCDO) are compared to the Mus musculus ADO (MmADO) sequence. Important ADO and PCO residues are highlighted in green, for CDO in blue, and key differences in yellow. All proteins possess a 3-His metal-binding motif marked by a ♦ and highlighted in gray. Additional motifs discussed in the text are denoted as follows: # Phe89 (MmADO numbering), ■ Cys-Tyr cross-link in MmCDO, ■ putative ADO and PCO cross-link motifs, • Cys120 and Cys169 in MmADO are replaced by Ser118 and Thr153 in PCO4, ▲ Asp192, * denotes a cis-peptide bond, and ♠ Tyr198 in MmADO and Tyr182 in AtPCO4 adjacent to the cis-peptide bond.
