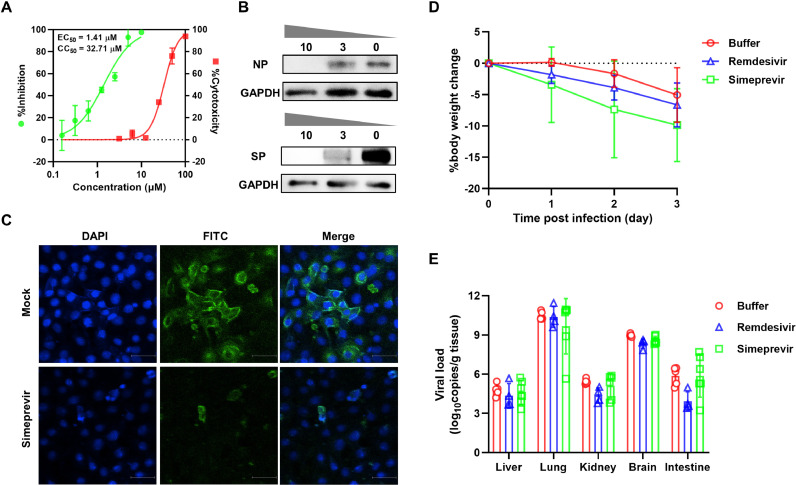
Fig. 1.
Effects of simeprevir on the replication of SARS-CoV-2. (A) Dose–response curve and cytotoxicity of simeprevir in Vero E6 cells. Cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 at an MOI of 0.01 in the presence of various doses of simeprevir for 24 h. Viral yield in the supernatant was quantified by RT-qPCR. The cytotoxicity of simeprevir against Vero E6 cells was determined by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay at simeprevir concentrations of 0–100 μM. (B) Western blot analysis of nucleocapsid protein (NP) and spike protein (SP) expression in SARS-CoV-2-infected cells pre-treated with 0, 3 and 10 μM simeprevir at 24 hpi. GAPDH was used as the reference gene. (C) Indirect immunofluorescence assay of SARS-CoV-2 in Vero E6 cells. Cells were infected with the virus at an MOI of 0.01 in the presence of 10 μM simeprevir for 24 h and were stained with a primary antibody specific for the SP. (D,E) Effects of simeprevir on the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vivo. For the in vivo antiviral assay, 12–14-week-old male hACE2 transgenic mice were intranasally inoculated with 105 TCID50 virus and were distributed into three groups (n = 6): simeprevir-treated; remdesivir-treated; and mock-treated (buffer). In the drug-treated groups, simeprevir 10 mg/kg and remdesivir 15 mg/kg were administered intraperitoneally at 4, 24 and 48 h after SARS-CoV-2 infection. The intraperitoneal volume for both drugs was 100 μL. The control group was treated with an equal volume of drug solvent buffer. Mice were continuously monitored for change in body weight and were euthanised at 72 hpi for viral load determination. Rapid weight loss was observed in all treatment groups (D). No significant difference in viral load was detected between the simeprevir-treated, remdesivir-treated and control groups (E). SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; MOI, multiplicity of infection; RT-qPCR, real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR; EC50, half-maximal effective concentration; CC50, 50% cytotoxic concentration; hpi, hours post-infection; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; hACE2, human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; TCID50, median tissue culture infectious dose.