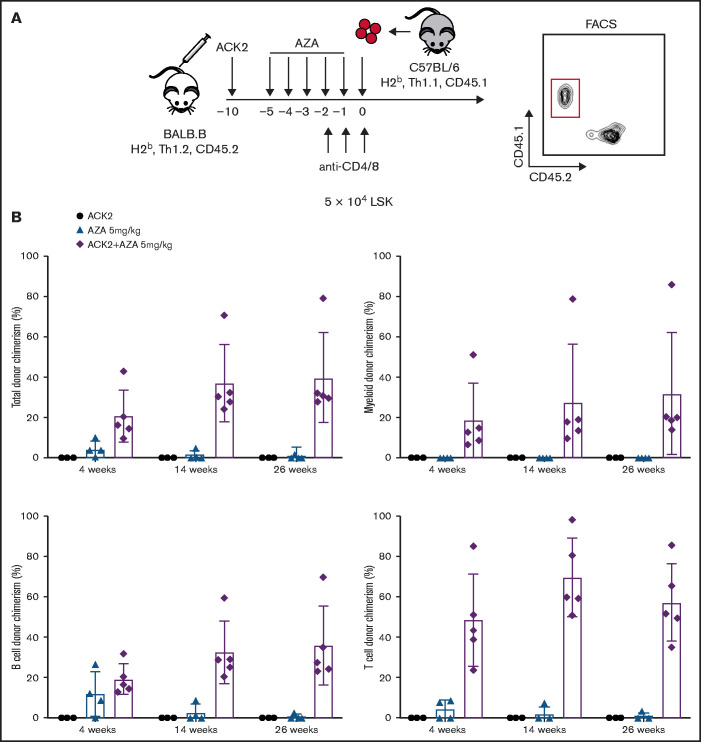
Figure 5.
ACK2 synergizes with AZA and permits engraftment of allogeneic HSCs in immunocompetent mice. (A) Schematic of allogeneic transplantations. BALB.B mice (H-2b, Thy1.2, CD45.2) were recipients for B6 donors (H-2b, Thy1.1, CD45.1). ACK2 was injected intravenously 10 days before transplantation, AZA was administered intraperitoneally on days −5 through −1 at 5 mg/kg per day, and anti-CD4/anti-CD8 mAbs were injected intravenously at 100 µg for each mAb on days −2, −1, 0 (day of transplant). Recipients received 5 × 104 LSK cells at day 0 via retro-orbital injection. PB chimerism analysis was assessed by flow cytometry using a CD45 marker to distinguish between donor and recipient live total, myeloid (Gr1+Mac1+), B cells (CD19+CD3–), and T cells (CD19–CD3+). (B) Multilineage donor-derived chimerism in PB at 4, 14, and 26 weeks after conditioning with single-agent ACK2, single-agent AZA 5 mg/kg per day, or ACK2-AZA and transplantation of 5 × 104 LSK cells. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 3-5 mice per group).