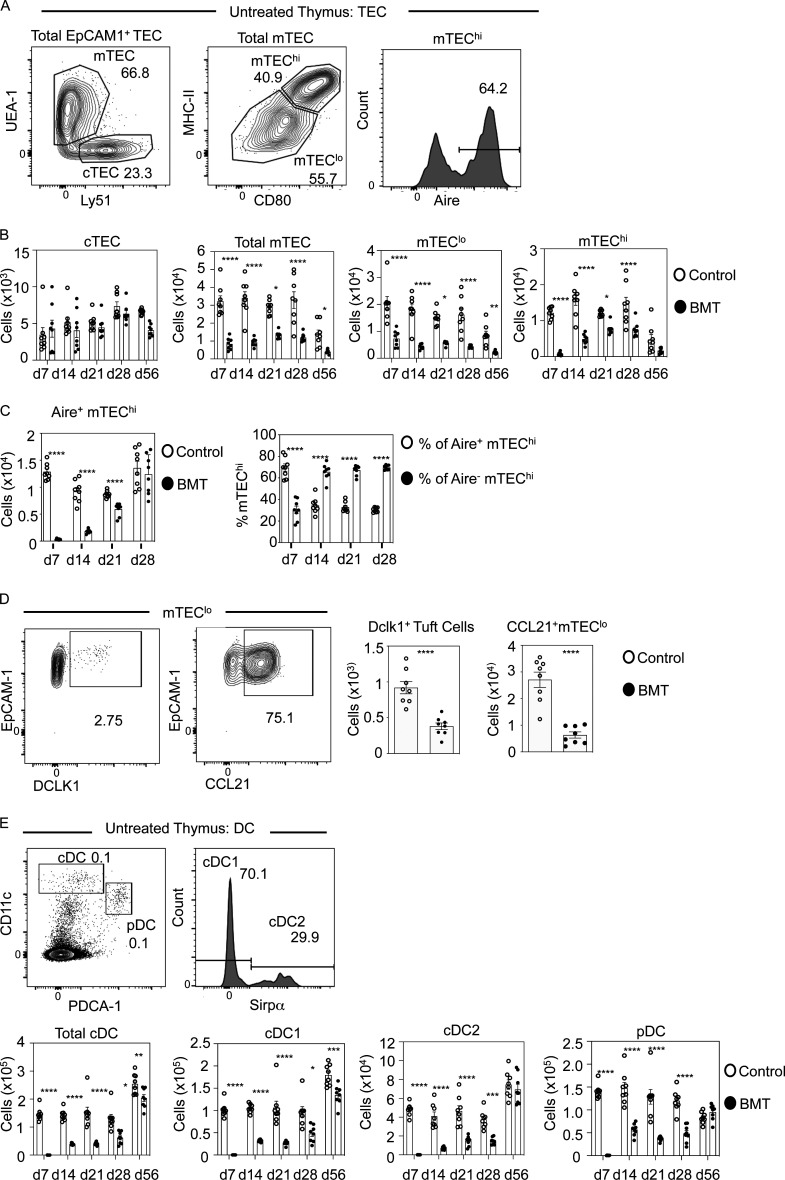
Figure 1.
Selective and sustained failures in thymus medulla regeneration during BMT-mediated immune reconstitution. (A) Gating strategy for TEC subsets in control and post-transplant thymus tissue. (B) Quantitation of TEC subsets in control (white dots) and BMT (black dots) mice. Controls are age-matched cohorts of unmanipulated mice taken at each time point alongside transplanted mice. Data represent three experiments, eight mice for each time point. d, day. (C) Quantitation of number of Aire+ mTEChi cells in control (white dots) and after BMT (black dots) and proportions of Aire+ or Aire− cells within mTEChi. (D) Representative FACS plots of DCLK1 or CCL21 expressing mTEClo with quantitation of these in control (white dots) and BMT mice (black dots); n = 8 across two independent experiments. (E) Gating strategy to detect thymic PDCA-1+ plasmacytoid DC, Sirpα− cDC1, and Sirpα+ cDC2 in control and post-transplant mice with quantitation of thymic DCs in control (white bars) and BMT (black bars) mice. Data from three separate experiments, n = 8 each time point. Error bars indicate SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.