Figure 7:
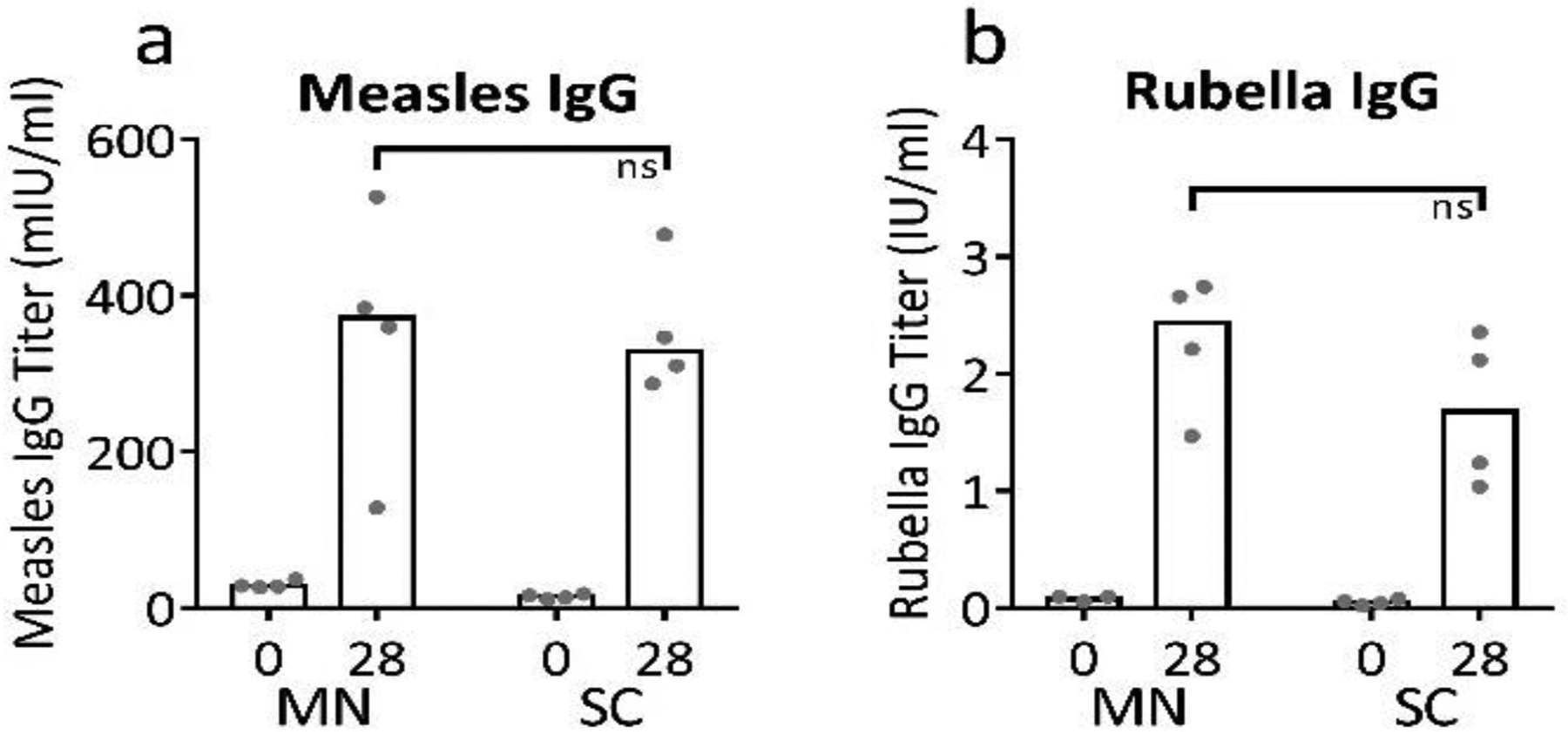
Immunogenicity of bivalent microneedle (MN) patches containing measles and rubella vaccines in non-human primates. Rhesus macaques were vaccinated by subcutaneous (SC) injection (n=4) or via MN patches formulated with sucrose, threonine, and potassium phosphate buffer at pH 7.5 (n=4). Serum IgG titers specific to measles (a) or rubella (b) were measured by ELISA. At 28 days post vaccination, titers between the two groups are not statistically different (Student’s t-test, p=0.95 and 0.22 for measles and rubella, respectively, ns = not significant). Data are expressed as bars to indicate the mean and with dots for individual rhesus macaques based on 4 replicates each.
