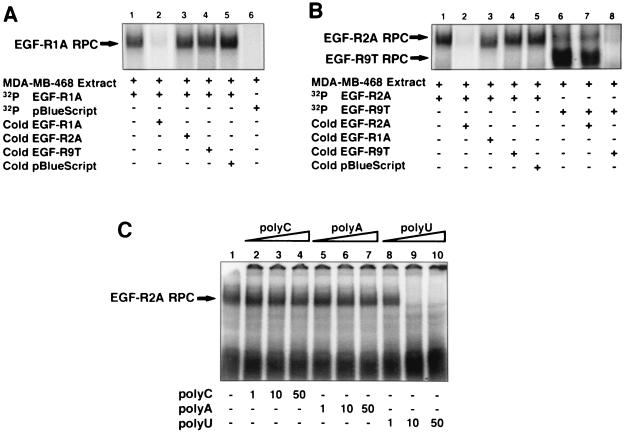
FIG. 6.
Proteins from MDA-MB-468 cells bind specifically to EGF-R mRNA. (A) MDA-MB-468 cytoplasmic extract (∼5 μg) was incubated with either 32P-labeled EGF-R1A (lanes 1 to 5) or pBlue riboprobe (lane 6), and REMSA was performed as described in Materials and Methods. In lanes 2 to 5, ∼100-fold excess unlabeled (cold) competitor RNA was added to the labeled EGF-R1A probe for 10 min at 22°C before addition of extract and REMSA. Arrow denotes RNA-protein complex (RPC). (B) MDA-MB-468 extract (∼5 μg) was incubated with either 32P-labeled EGF-R2A (lanes 1 to 5) or EGF-R9T (lanes 6 to 8), and REMSA was performed as above. In lanes 2 to 5, 7, and 8, ∼100-fold excess of various unlabeled competitor RNA was added to the labeled probe prior to the extract. Arrows denote RNA-protein complexes (RPC). (C) MDA-MB-468 extract was incubated with labeled EGF-R2A in the absence (lane 1) or presence of increasing concentrations (1, 10, and 50 ng) of unlabeled homopolymers RNA, poly(C) (lanes 2 to 4), poly(A) (lanes 5 to 7), and poly(U) (lanes 8 to 10). Arrow denotes RNA-protein complex (RPC). The data are representative of at least three individual experiments.