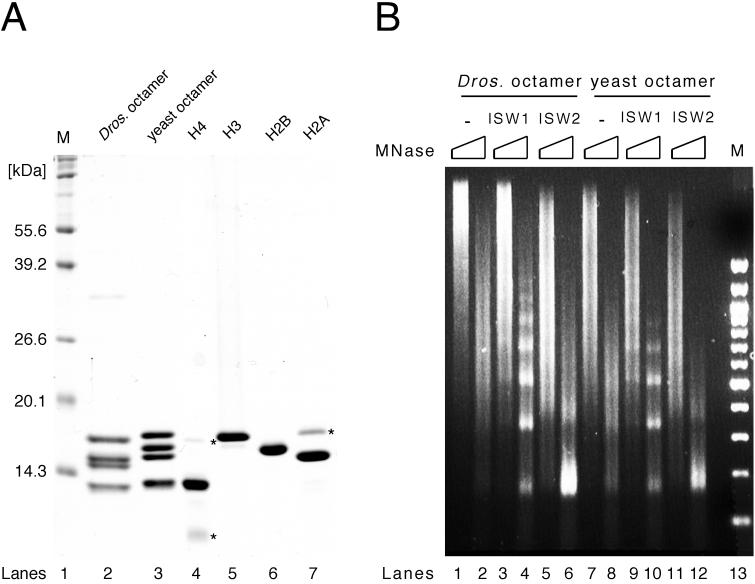
FIG. 1.
Reconstitution of recombinant yeast histone octamer. (A) Purified recombinant yeast core histones and histone octamer. Yeast core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) were expressed and purified individually from E. coli (lanes 4 to 7). Reconstituted recombinant yeast histone octamer (lane 3) is shown next to native Drosophila histone octamer (lane 2) for comparison. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE (15% gel) and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R250. Lane M, size markers; ∗, minor contaminant present after purification of individual core histones. (B) Isw1 and Isw2 complexes facilitate the formation of regularly spaced nucleosomes assembled with recombinant yeast histone octamer. Nap1p-mediated nucleosome spacing assays using Drosophila (left) or yeast (right) histone octamer were performed on lambda DNA in the presence or absence of Isw1 and Isw2 complexes. All reactions contained ATP. Nucleosome spacing was analyzed by partial and extended MNase digestion. DNA was purified and separated by 1.3% agarose gel electrophoresis followed by ethidium bromide staining.