Figure 3.
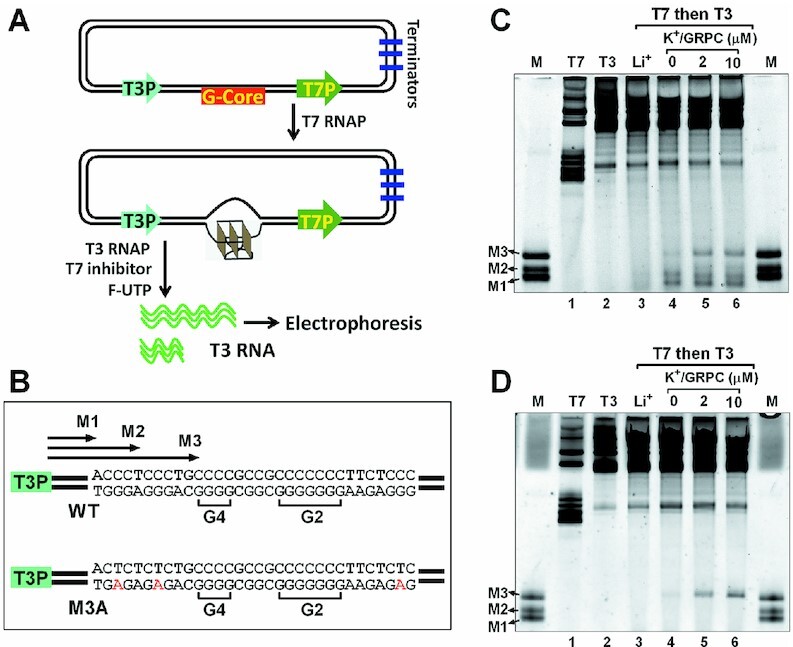
Detection of GVBQ in the wild G-rich dsDNA from the PDGFR-β promoter NHE region by RNA polymerase arrest. (A) Plasmid contained the PDGFR-β gene promoter G-core sequence, a T7 and a T3 promoter. The G-core sequence was placed at the upstream of T7 promoter and downstream of T3 promoter. The plasmid was first transcribed with T7 RNA polymerase to induce the formation of G-quadruplexes, and then T3 RNA polymerase was added together with a fluorescein-UTP and a T7 inhibitor to produce fluorescent T3 RNA transcripts. The T7 inhibitor was used to prevent the T7 RNA polymerase from further transcription. (B) Sequences of WT and mutant M3A G-core. (C) Detection of G-quadruplexes in the WT plasmid by the premature termination of T3 RNA polymerase. Marker (M) shows termination sites labeled in B. (D) Detection of a G-quadruplex in the mutant M3A plasmid by the premature termination of T3 RNA polymerase.
