Figure 3.
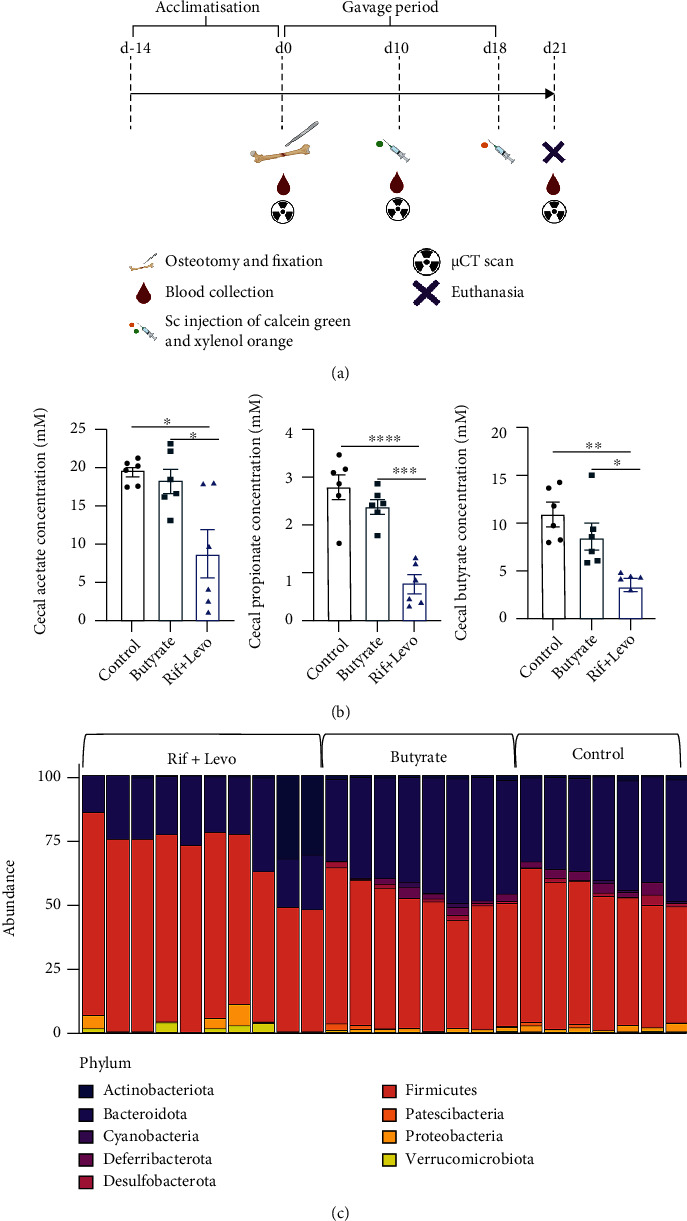
Rifampicin- and levofloxacin-treated mice show reduced cecal SCFA levels and a change in gut microbiome composition compared to butyrate- and control-treated mice. The effect of butyrate on the gut microbiome, systemic immunity, and bone healing was assessed in a murine osteotomy model. (a) Experimental outline of in vivo study indicating interventions and time frame. The figure was created with http://BioRender.com/. (b) Cecal concentrations of acetate, propionate, and butyrate were measured by means of UPLC. Data shown are means (n = 6) and ±SEM. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗p < 0.05. (c) DNA of murine cecal content was isolated, and 16s rRNA sequencing was performed to determine microbiome composition. Percent abundance of bacterial phyla in the murine cecum (n = 10Rif + Levo-treated animals, n = 8 butyrate-treated animals, and n = 7 control-treated animals).
