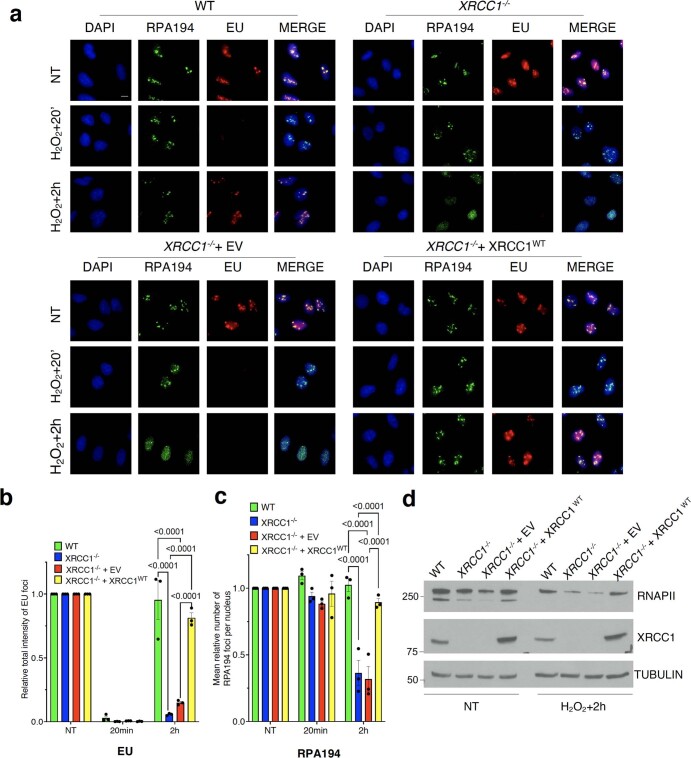
Extended Data Fig. 2. XRCC1 promotes the recovery of transcription following oxidative damage.
a, Representative images of the RNAPI foci (RPA194) and levels of global transcription (EU immunofluorescence) in WT and XRCC1−/− U2OS cells stably transfected with either empty vector (EV) or expression construct encoding full length C-terminal histidine-tagged XRCC1 (XRCC1WT), following mock treatment or at the indicated times after treatment with 1 mM H2O2 for 20 min. Scale bars, 10 μm. b and c, Quantification of the RNAPI foci (RPA194) and levels of global transcription (EU immunofluorescence) shown in (a). Data are means (±s.e.m.) of three independent experiments, and statistically significant differences were determined by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (p values are indicated). d, Immunoblot of RNAPII hyperphosphorylation in WT U2OS cells, XRCC1−/− U2OS cells, and XRCC1−/− U2OS cells stably transfected with either empty vector (EV) or expression construct encoding full-length histidine-tagged XRCC1 (XRCC1WT), following mock treatment or 2 h after treatment with 1 mM H2O2 for 20 min. A representative blot from one of three independent experiments is shown.