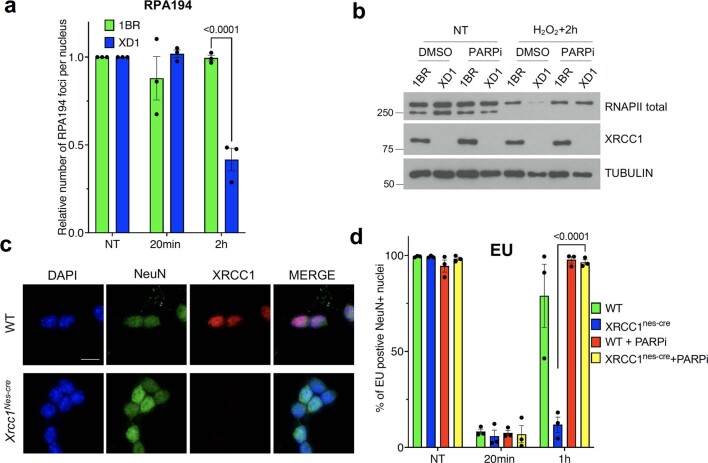
Extended Data Fig. 4. Toxic PARP1 activity suppresses transcriptional recovery in XRCC1 patient fibroblasts and Xrcc1-deficient mouse cerebellar neurons.
a, Quantification of the RNAPI foci (RPA194) shown in (Fig. 3a). Data are means (±s.e.m.) of three independent experiments, and statistically significant differences were determined by two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (p values are indicated). b, Immunoblot of RNAPII hyperphosphorylation in normal fibroblasts (1BR) and XRCC1 patient fibroblasts (XD1) following mock treatment or 2 h after treatment with 60 μM H2O2 for 5 min. Cells were incubated with DMSO vehicle or with 10μM PARP inhibitor (PARPi) for 1 h prior to, during, and following H2O2 treatment as indicated. A representative image from one of three independent experiments is shown. c, XRCC1 and NeuN immunofluorescence in WT and Xrcc1nes-cre mouse cerebellar neurons. Scale bars, 10 μm. d, Quantification of the levels of global transcription (EU immunofluorescence) shown in (Fig. 3c). Data are means (±s.e.m.) of three independent experiments, and statistically significant differences were determined by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.