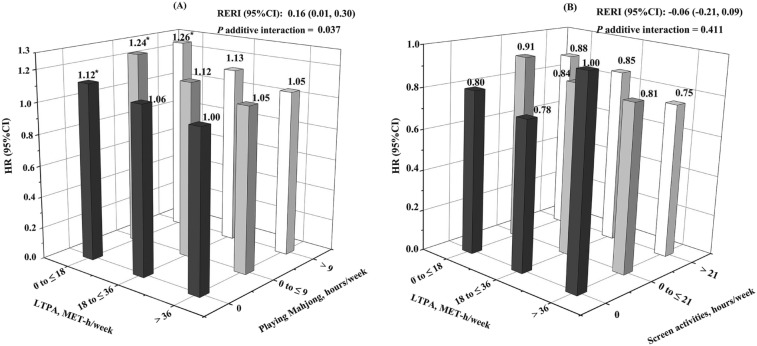
Figure 3.
The joint effect of LTPA and sedentary behavior on incident CVD. (A) The joint effect of LTPA and Mahjong playing on incident CVD. (B) The joint effect of LTPA and screen activities on incident CVD. The multivariable models were adjusted for age, sex, education, smoking status, alcohol intake, consumption of food (meat, vegetables, and fruit), hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, BMI, MET-hours/week, and family history of CVD. *P < 0.05. †The number was 26,354 for Mahjong and incident CVD analysis; the number was 26,558 for screen activities and incident CVD analysis. ‡The hazard ratios (95% CI) from the most active to the least active group were: 1 (reference), 1.06 (1.00 to 1.16), 1.12 (1.01 to 1.24), 1.05 (0.90 to 1.21), 1.12 (0.96 to 1.30), 1.24 (1.07 to 1.44), 1.05 (0.90 to 1.21), 1.13 (0.97 to 1.32), 1.26 (1.08 to 1.47), respectively, in (A). ¶The hazard ratios (95% CI) from the most active to the least active group were: 1 (reference), 0.78 (0.45 to 1.35), 0.80 (0.51 to 1.25), 0.81 (0.57 to 1.14), 0.84 (0.59 to 1.19), 0.91 (0.64 to 1.30), 0.75 (0.53 to 1.07), 0.85 (0.60 to 1.22), 0.88 (0.61 to 1.25), respectively, in (B).