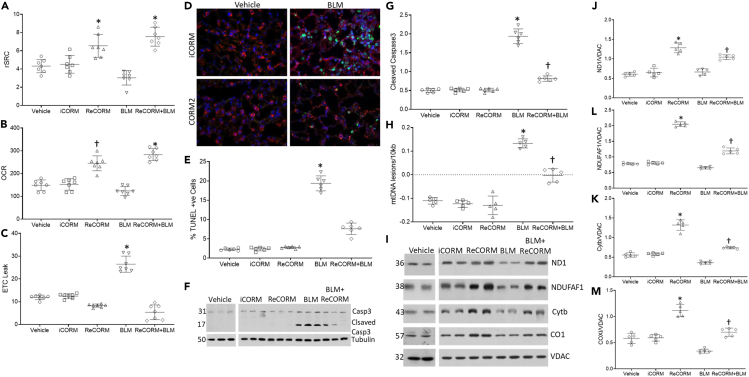
Figure 4.
Mitochondrial abnormalities and cell death in alveolar epithelial cells after BLM
(A) Oxygen consumption rates (OCR) measured in isolated AT2 cells.
(B) Spare respiratory capacity is the difference between OCR of cells treated with CCCP and untreated cells.
(C) ETC leak rate.
(D) TUNEL analysis of lungs from mice following BLM treatment. Fluorescent sections were analyzed by confocal microscopy, TUNEL positive nuclei, and stain green demonstrating severe cellular injury with DNA damage. SpC reagent stains respiratory epithelial cells red, and nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). Magnification, × 400.
(E) Scatterplots of quantification of TUNEL staining. Number of positive cells/500 random respiratory epithelial cells.
(F) Immunoblot of lung caspase 3 cleavage.
(G) Scatterplots of densitometry analysis for Caspase 3.
(H) BLM induced mtDNA damage. Oxidized mtDNA, occurring predominantly in the long 10kb mtDNA fragment. The Scatterplots show mtDNA lesion frequency in mouse lung. MtDNA lesions increased in BLM treated animals, but are suppressed by ReCORM treatment.
(I) Lung tissue immunoblots showing levels of NDI and NDUFAF1 (Complex I), Cytb (Complex III), and COX1 (Complex IV) protein.
(J–M) Scatterplots of densitometry analyses of NDI and NDUFAF1, Cytb, and COX1 normalized to an outer mitochondrial membrane protein VDAC. N = 6 mice per group, data are means ± SD of four independent experiments, ∗P < 0.05 compared RECORM with the iCORM group. †P < 0.05 ReCORM + BLM vs BLM groups.