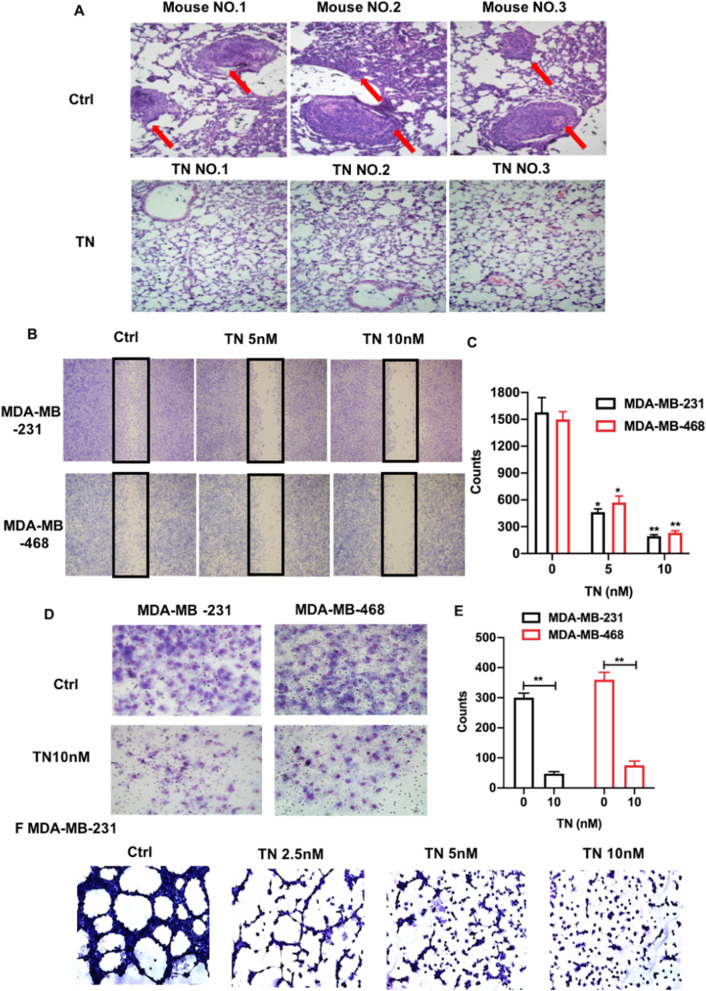
Fig. 2.
Triptonide notably inhibits TNBC cell invasion and lung metastasis. The lungs in triptonide (TN)-treated and control (Ctrl) mice were fixed, subjected to H&E staining, and imaged with a microscope (400 ×). Tumors were appeared in the lung tissues of control mice (A, up panels), but were absent in the lung tissues of TN-treated mice (A, low panels). The numbers of migrated MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells in the wounded area were first imaged and counted; then, the cell migration-inhibitory rate was calculated (B, C). Cell invasion was performed by a trans-well system. MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells in the bottom chamber that invaded from the up chamber were fixed, stained with Wright–Giemsa solution, imaged using OLYMPUS CKX31 microscope (D), and statistically analyzed (E). The tumor cell tube-forming assay showed that TN at the concentration of 10 nM almost completely inhibited MDA-MB-231 cell formation of capillary like structures (G). The results represent three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01