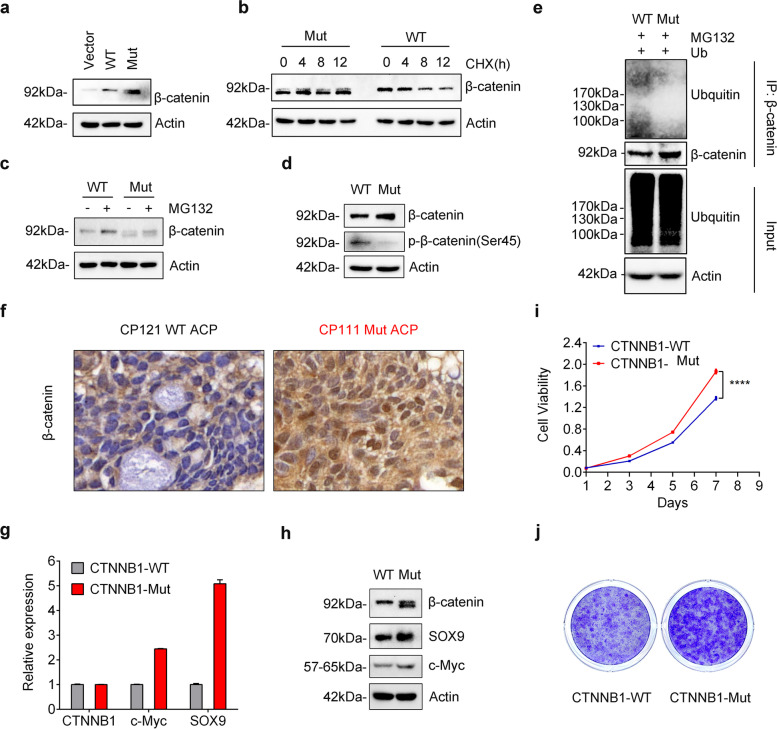
Fig. 5.
CTNNB1-Mut promote ACP primary cell proliferation by activating Wnt target genes. (a) Western blotting was performed to verify the overexpression of CTNNB1-WT and CTNNB1-Mut in ACP primary cells. (b) CTNNB1-WT/Mut ACP primary cells were treated with CHX (50 μg/ml) for 0, 4, 8, 12 h, followed by IB using anti-β-catenin and actin antibodies. (c) CTNNB1-WT/Mut ACP primary cells were treated with 10 μM MG132 for 10 h, and β-catenin expression levels were determined by western blotting. (d) CTNNB1-WT/Mut ACP primary cells were treated with 50 nM Calyculin A for 30 min. The cell lysate was IB with anti-β-catenin and anti-β-catenin-phosphate-S45 antibodies. (e) Ubiquitin was transfected into CTNNB1-WT/Mut ACP primary cells. After 48 h, cells were treated with 10 μM MG132 for 10 h. Cell lysates were subjected to IP with anti-β-catenin followed by IB with ubiquitin or anti-β-catenin antibody. (f) IHC of β-catenin in CP121 (CTNNB1 wild type in patient tissue), CP111 (CTNNB1 deletion mutants in patient sample), scale bars: 50 μm. (g-h) The mRNA (g) and protein (h) levels of SOX9 and c-Myc were examined in CTNNB1-WT/Mut ACP primary cells. (i-j) CCK8 assay (i) and colony-formation experiments (j) were performed to assess cell proliferation in the CTNNB1-WT/Mut in ACP primary cells. The results are shown as mean ± SD; *, P < 0.05; two-tailed Student t-test