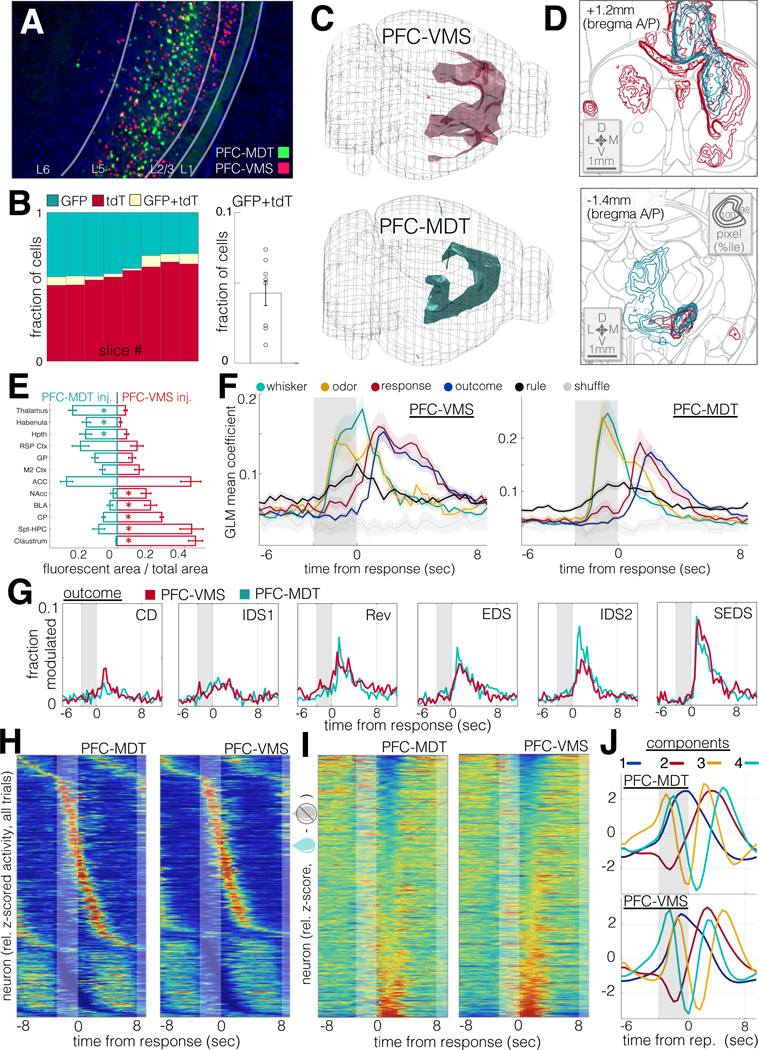
Figure 5: PFC-VMS and PFC-MDT projection populations exhibit similar task response properties.
A. Dual PFC-VMS and PFC-MDT projection labeling in a single preparation. Green: rAAV2-CAG-mGreenLantern in MDT; red: AAV9-CAG-F3/FRT-NLS-tdTomato in PFC and CAV2-FLP in VMS (DAPI in blue).
B. Cell counts by slice from the experiment in (A). Left: relative green, red, and double-labeled cell counts. Right: median relative overlap (N=8 sections, 2 animals).
C. Composite images of long-range axon projections from PFC-VMS (N=5 animals) and PFC-MDT (N=5 animals) labeling (see Methods). Volumes shown are thresholded to ≥98th percentile for pixel brightness.
D. Coronal sections and contour plots of fluorescent axon density in PFC-VMS (top) and PFC-MDT (bottom) labeled animals. Top: a composite (N=5 animals) of pixel brightness in a coronal cross-section centered on the nucleus accumbens. Concentric contours correspond with relative pixel brightness. Bottom: composite (N=5 animals) of pixel brightness in a coronal cross-section centered on medial thalamus. Contour brightness scale as in (top).
E. Mean ± SEM plots showing the fraction of pixels in each region showing fluorescence above the threshold percentile. 2-way ANOVA revealed an interaction effect between injection type and region (F=17.96, p=0). Post-hoc t-tests revealed significant differences (unpaired t-test p<0.01) for thalamus, habenula, caudoputamen, septo-hippocampal complex, and claustrum, and p<0.02 for hypothalamus, basolateral amygdala, and nucleus accumbens.
F. Trial-aligned SVM decoder accuracy for whisker stim, odor stim, response, outcome and rule. N=1770 units from 8 animals (PFC-VMS, left), and N=1155 units from 9 animals (PFC-MDT, right).
G. Histograms traces of the fraction of cells modulated (rank sum p<0.01) by trial outcome over trial-aligned timepoints and through learning stages for PFC-VMS (red) and PFC-MDT (green) neurons.
H. Trial-averaged activity histograms for PFC-VMS (left) and PFC-MDT (right) cells. Each cell’s mean trace is normalized to its peak value, and cells are sorted by time of peak excitation (top) or inhibition (bottom).
I. Mean outcome difference (incorrect – correct) traces for PFC-VMS and PFC-MDT neurons. Each cell’s mean difference trace is normalized to its peak value, and cells are sorted from most strongly preferring correct outcomes (top) to incorrect outcomes (bottom).
J. First four principal components for trial-averaged activity histograms in PFC-MDT (top) and PFC-MDT (bottom) neurons.