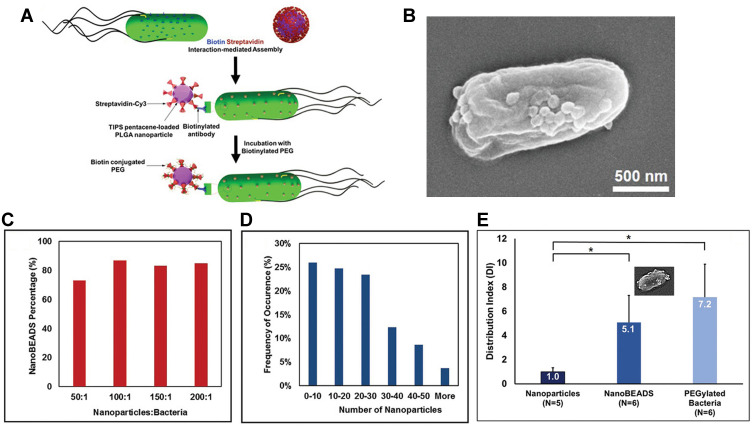
Figure 4.
The development of bacteria-enabled autonomous drug delivery system (NanoBEADS) via biotin-streptavidin conjugation. (A) Each NanoBEADS agent is constructed by conjugating several streptavidin-coated PLGA nanoparticles with a tumor targeting biotinylated-antibody coated S. typhimurium VNP20009, using streptavidin–biotin noncovalent affinity-based bonds. NanoBEADS assembly was followed by incubation with mPEG-biotin to quench residual streptavidin binding sites on the nanoparticles. (B) A representative SEM image of a NanoBEADS agent. (C) Percentage occurrence of NanoBEADS formation at various nanoparticle:bacteria ratios used for NanoBEADS construction. (D) Distribution of nanoparticle loading of NanoBEADS agents constructed at nanoparticle to bacteria ratio of 100:1. (E) Distribution index (DI) of PLGA nanoparticles, NanoBEADS, and PEGylated bacteria in 4T1 tumors. Each NanoBEADS agent carries an average of 22 nanoparticles, thus, it enhances the intratumoral transport of nanoparticles by up to ≈100-fold (*p<0.05). Adapted from Suh S, Jo A, Traore MA, et al. Nanoscale Bacteria-Enabled Autonomous Drug Delivery System (NanoBEADS) enhancesintratumoral transport of nanomedicine. Adv Sci. 2019;6(3):1801309. © 2018 The Authors. Published by WILEY‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license.54