Fig. 6.
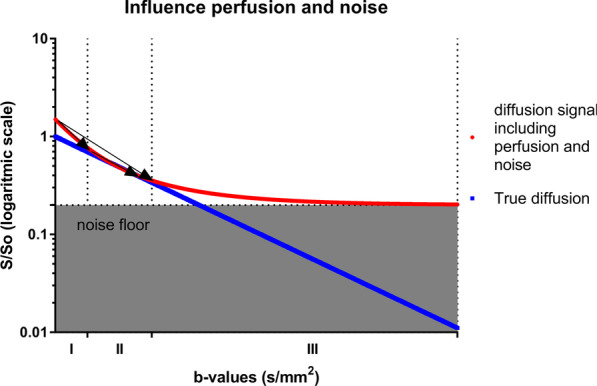
Schematic overview, with the semi logarithmic plots (and S0, the signal at b = 0 without perfusion component) of the signal attenuation of pure diffusion (blue curve) and signal attenuation by (micro)perfusion, diffusion and including contribution of noise by the rician noise floor (red curve). Within the red curve, the first small arrow represents the mono-exponential slope (ADC1) within segment I, the second small arrow includes the mono-exponential slope in segment II (with ADC2). The large arrow represents the mono-exponential approach/slope (ADC3) using two b-values, one in segment I and one in segment II. Three segments of diffusion sensitive gradient strength, by the b-values are defined; I: diffusion and flow-sensitive b-values (diffusion gradients); II: diffusion sensitive, flow insensitive b-values; III: flow insensitive and noise sensitive b-values. The b-value independent rician noise level is mentioned as noise floor. Note: ADC1 + ADC2 = ADC3. The axis scales, slopes and by this the numeric functions are used as a schematic representation for the general picture and therefore might differ from clinical practice
