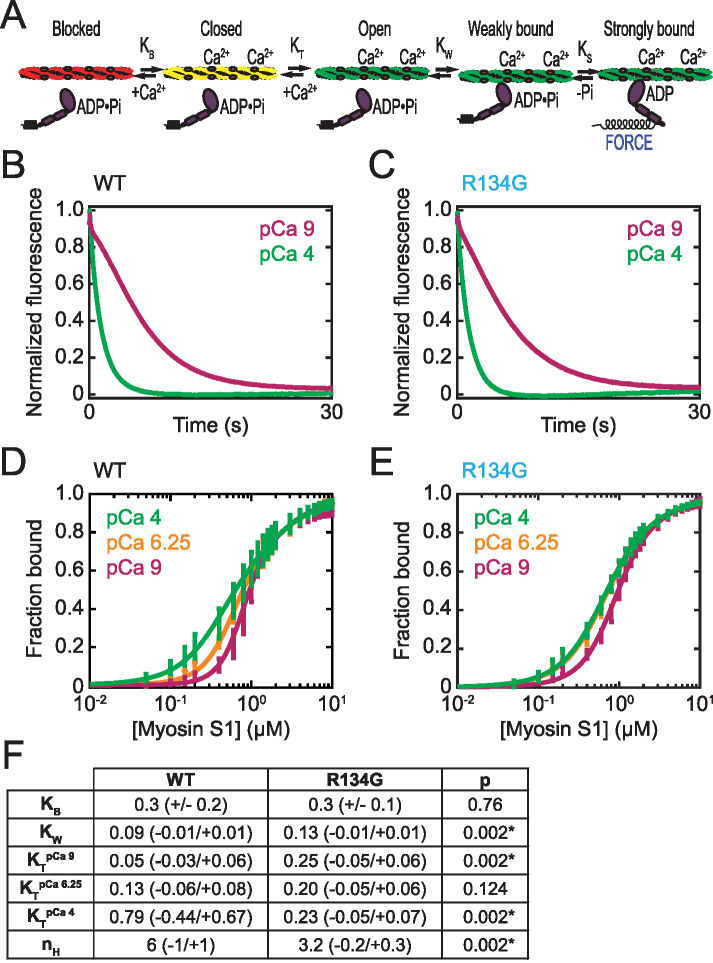
FIGURE 5:
Effects of R134G on tropomyosin positioning along the thin filament. (A) Schematic of the three-state model of thin filament regulation. The equilibrium constants KB and KT describe the blocked-to-closed and closed-to-open transitions of the thin filament, respectively. KW and KS describe weak and strong myosin binding, respectively. (B, C) Measurement of KB. Stopped-flow kinetic traces of myosin S1 binding to RTFs containing pyrene-actin and WT (B) or R134G (C) troponin T. Traces are the average of 10 independent experiments, each the average of at least three technical replicates. S1 binding quenches the pyrene fluorescence at a higher rate at high calcium (pCa 4, green) than at low calcium (pCa 9, magenta) in each case. The value of KB was determined using Eq. 1 (Materials and Methods). (D, E) Measurement of KT and KW. Steady-state titrations of RTFs with S1 for WT (D) and R134G (E) at three calcium concentrations: saturating (pCa 4, green), intermediate (pCa 6.25, orange), and low (pCa 9, magenta). Curves are fits of Eq. 2 (Materials and Methods) to the data. Error bars represent the SD of six technical replicates collected on six independent experimental days. (F) Table of parameter values determined for WT and R134G. KB was determined from the stopped-flow measurements and is given as the average ± SD of 10 replicates. All other parameters were determined from the steady-state titrations and are given as best-fit values with 95% confidence intervals. Asterisks indicate statistical significance at the 95% confidence interval.