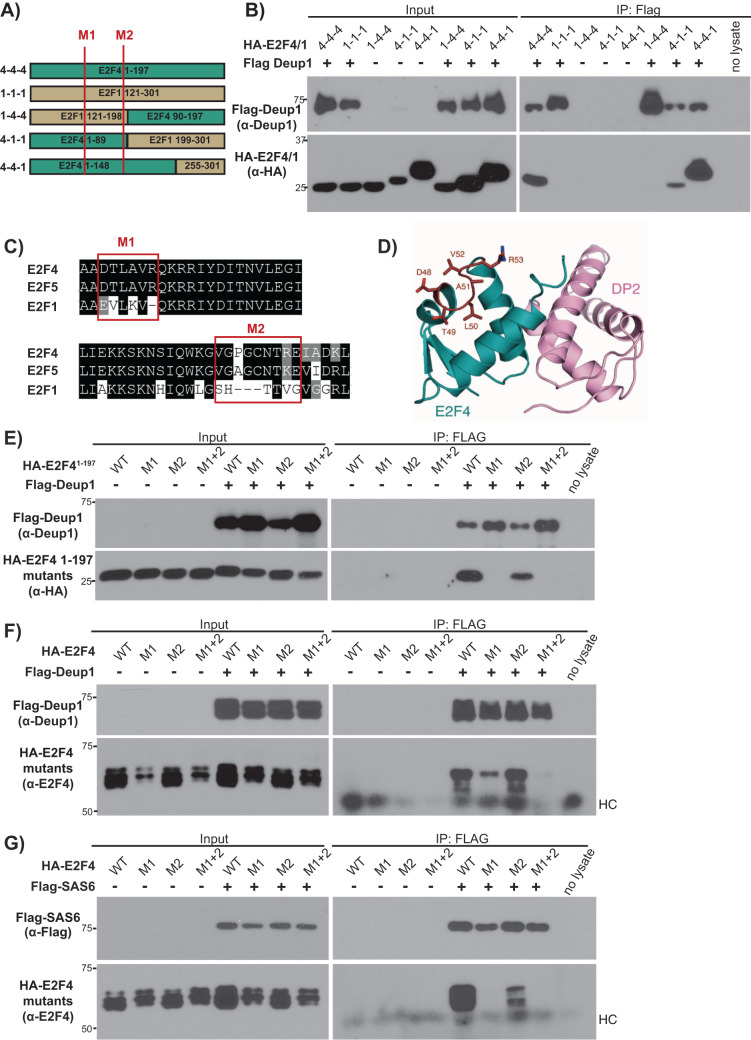
FIGURE 6:
Efficient Deup1 and SAS6 binding requires a short motif (E2F448–53) that is conserved in E2F4 and E2F5 but not other E2Fs. (A) Schematic representation of E2F41–197, E2F1121–301 and the various E2F4/E2F1 chimeras. Red lines show the positions of the M1 and M2 mutations. (B) Cell lysates containing HA-tagged E2F4/E2F1 chimeras (HA-E2F4/1), alone or with Flag-Deup1 were subjected to Western blotting with the indicated α-Deup1 or α-HA antibodies before (Input) or after IP with α-Flag antibodies. (C) Amino acid alignments of E2F4, E2F5 and E2F1 with the red boxes indicating the M1 and M2 motifs, which were swapped from E2F4 to E2F1 sequences in the M1 and M2 mutants. (D) Crystal structure of the E2F4 DBD illustrating the exterior surface position of the M1 site (in red). The M2 mutation site is C-terminal to the structured DBD region and was unresolved in the crystal structure (Zheng et al., 1999). (E–G) Cell lysates with the indicated WT, M1, M2 or M1+2 versions of (F, G) HA-tagged full-length E2F4 or (E) HA-E2F41–197, expressed alone or with (E, F) Flag-Deup1 or (G) Flag-SAS6, were subjected to Western blotting with the indicated (E, F) α-Deup1, (G) α-Flag, (E) α-HA, and (F, G) α-E2F4 antibodies before (Input) or after IP with α-Flag antibodies. For F and G, HC denotes the heavy chain of IgG.