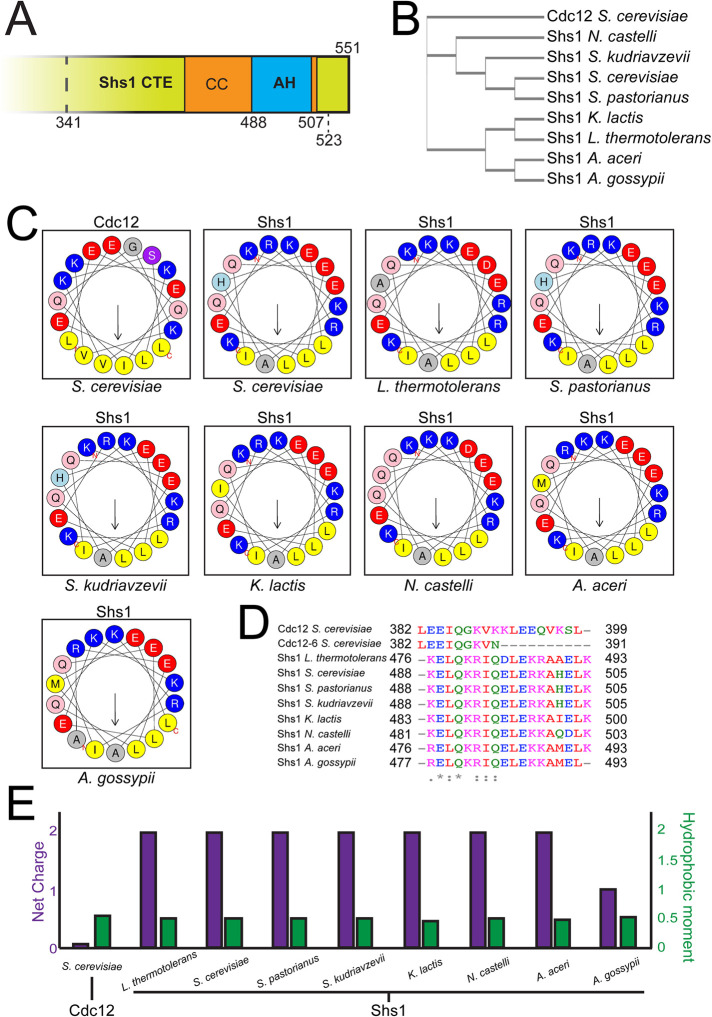
FIGURE 1:
Shs1 contains a highly conserved amphipathic helix within its C-terminal domain. (A) cerevisiae Shs1 CTE with a predicted AH domain within the coiled coil. Truncation alleles within Shs1 CTE demarcated (discussed in Figure 3). (B) Cladogram constructed from multiple alignments of Shs1 primary sequences from various ascomycetes compared with Cdc12 from S. cerevisiae. (C) Helical wheels representing amphipathic helices present in septin polypeptides screened ascomycetes. Residues in blue: basic amino acid; red: acidic; yellow: hydrophobic; gray: small side chain; light blue: histidine; pink: asparagine or glutamine; purple: serine or threonine. (D) Sequence alignment of amphipathic helices with indicated residue numbers. Residues in red: hydrophobic, magenta: basic; blue: acidic; green: uncharged. (E) Net charge and hydrophobic moment of septin amphipathic helices.