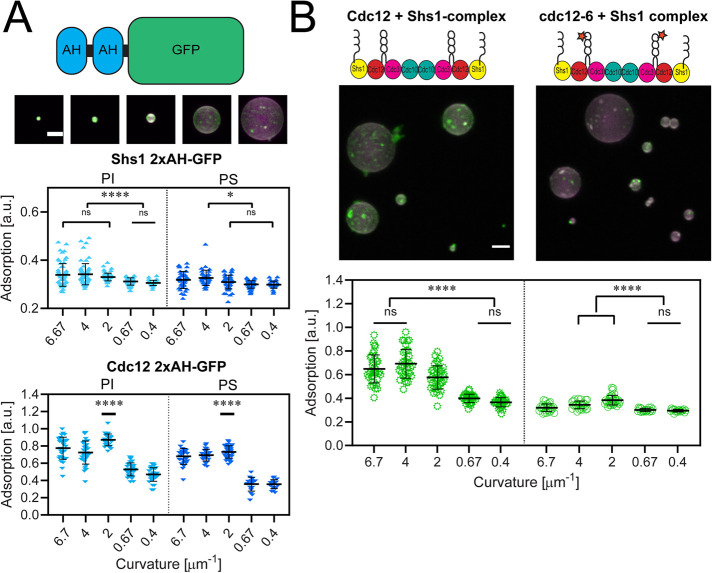
FIGURE 2:
Shs1’s amphipathic helix is capable of binding micron-scale membrane curvatures. (A) Top, cartoon depiction of a 2xAH-GFP construct. Middle, maximum projection images of 1.25 µM Shs1 2xAH-GFP (green) adsorbed onto curved supported lipid bilayers (74.5% DOPC, 25% PI, 0.5% rhodamine-PE; magenta). Scale bar, 2 µm. Images contrasted identically. Bottom, plots of 2xAH-GFP peptide adsorption to supported lipid bilayers with different curvatures based on silica bead sizes (as in the image above). Top plot is the Shs1 2xAH-GFP peptide, and the bottom plot is the Cdc12 2xAH-GFP peptide. Experiments on PI membranes (composition is 74.5% DOPC, 25% PI, 0.5% rhodamine-PE) are in light blue, whereas PS membranes (composition is 74.5% DOPC, 25% PS, 0.5% rhodamine-PE) are dark blue. Curvatures (in μm−1) of 6.7, 4, 2, 0.67, and 0.4 represent bead diameters of 0.3, 0.5, 1, 3, and 5 μm, respectively. Each point represents the measured adsorption ratio (GFP fluorescence normalized to lipid fluorescence) on an individual bead (≥30 beads measured across three replicates at each curvature). Black bar represents mean. Error bars represent the SD of the mean. ns, adsorption was not significantly different; *, adsorption was significantly different (p < 0.01); **, p < 0.0053); ****, p < 0.0001. (B) Top, maximum projection images of 50 nM wild-type Cdc12 + Shs1 septin complex (green, panel 1) and mutant cdc12-6 + Shs1 complex (green, panel 2) on curved supported lipid bilayers (magenta). Uneven adsorption of septin complexes on individual beads reflects localized differences in the extent of septin filament polymerization on the supported lipid bilayer. Scale bar, 2 µm. Images are contrasted identically. Bottom, plots quantifying adsorption onto different curvatures (membrane composition is 74.5% DOPC, 25% PI, 0.5% rhodamine-PE). Black bars represent the mean. Error bars are the SD for n ≥ 30 beads at each curvature across three replicates. ns, adsorption was not significantly different; ****, adsorption was significantly different (p < 0.0001).