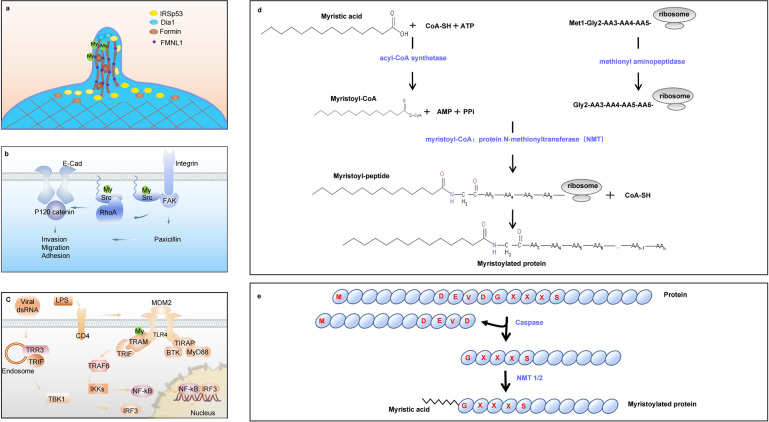
Fig. 2.
Schematic representation of protein N-myristoylation and function. a The myristoylation of formin family protein FMNL1 leads to membrane association, membrane trafficking and bleb formation. b The N-terminal myristoylation is essential for the membrane attachment and kinase activity of Src. c The myristoylated TRAM tethers it to the membrane, serving as a prerequisite for LPS signaling. d Co-translational N-myristoylation. The initiator methionine is removed by methionine aminopeptidase 2 and myristic acid is transferred to the N-terminal glycine residue by NMT. e Post-translational N-myristoylation. Some proteins are cleaved by a protease to facilitate a myristic acid is covalently attached to glycine residue by NMT