Fig. 3.
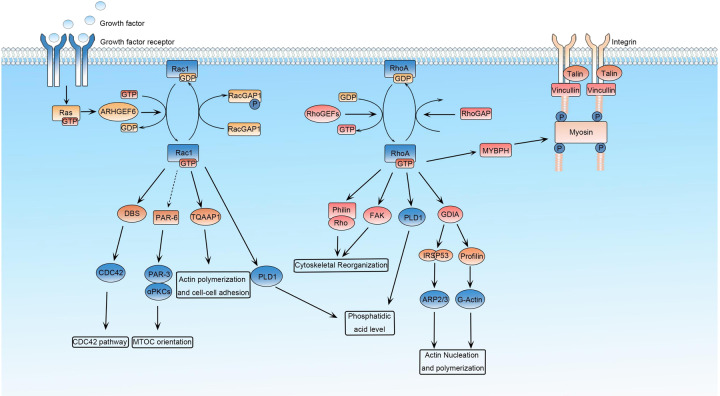
Ras is a membrane-associated guanine-nucleotide-binding protein that is normally activated in response to the binding of growth factors. Rac1 is a small G-protein in the Rho family that drives MTOC orientation, actin polymerization, and cell–cell adhesion. Rac1 is activated by ARHGEF6 and repressed by RacGAP in response to upstream regulators such as growth factors. Rho is a member of the Ras superfamily of small GTP-binding proteins that play a central role in diverse biological processes. Rho proteins cycle between an active GTP-bound state and an inactive GDP-bound state, which is controlled by regulatory proteins such as GEFs (guanine exchange factors and GAPs (GTPase-activating proteins). The GTPase RhoA plays a prominent role in regulating the organization of the cytoskeleton by promoting the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers and by activating FAK. PLD1 catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine to yield phosphatidic acid and choline. Rho also activates scaffolding proteins such as GDIA and IRSp53 (insulin receptor substrate protein-53). RhoA also binds to Rho/philin and regulate the actin cytoskeleton. The Rho family members Rac1, RhoA, and CDC42 were reported geranylgeranylated, and Ras was reported farnesylated to regulate their cellular functions