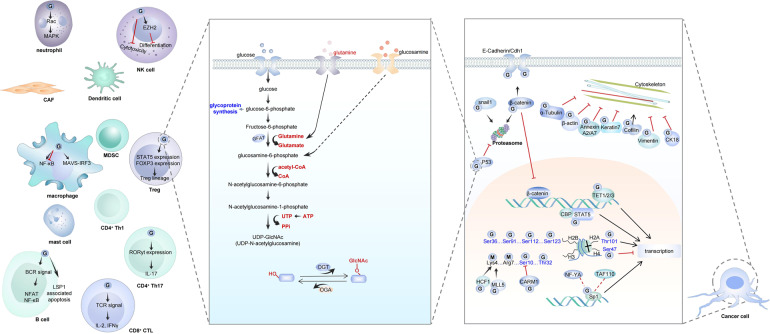
Fig. 5.
Overview of the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (HBP) and the regulation of O-GlcNAcylation in TME. Left: O-GlcNAcylation orchestrates immunity. O-GlcNAcylation is increased after neutrophils are activated through the MAPK pathway. In macrophages, O-GlcNAcylation shows both activation and inhibition functions of NF-κB. Upon RNA virus infection, MAVS is modified by OGT to enhance downstream IFN production via IRF3 signaling. O-GlcNAcylation reduces the cytotoxic activity and inhibits NK differentiation by increasing the stability of EZH2. O-GlcNAcylation increases the expression of RORγt and FOXP3 in Th17 and Treg cells. NFAT and NFκB are activated by O-GlcNAcylation in activated B cells and O-GlcNAcylation of LSP1 contributes to B-cell apoptosis. After TCR rearrangement, O-GlcNAcylation promotes positive T-cell development. Middle: nutrient flux modulates protein O-GlcNAcylation. OGT catalyzes the addition of GlcNAc from UDP-GlcNAc to serine and threonine residues, while OGA catalyzes their removal. Right: the function of O-GlcNAcylation in proteasome-associated degradation, cytoskeleton remodeling, and transcriptional regulation