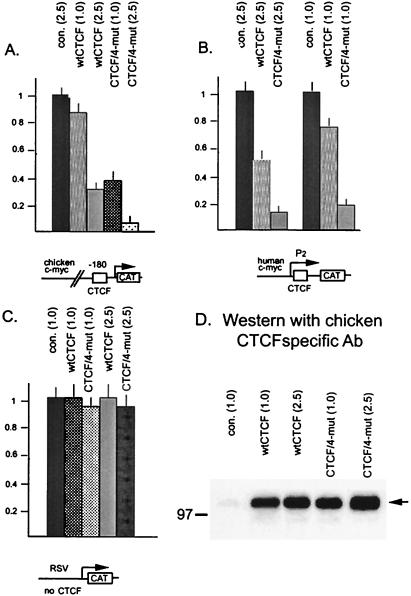
FIG. 9.
Mutating the carboxy-terminal CKII target serines converts CTCF to a stronger repressor of the chicken and human c-myc gene promoters bearing different target sites, CTS V (32) or CTS A (20), respectively. Specific CTCF-binding promoter-reporter constructs, the pPst2myc-CAT plasmid containing 3.3 kb of the 5′ noncoding region of the chicken c-myc (A) or the P2 promoter-containing pP2myc-CAT plasmid (B), were utilized. The pRSV-CAT construct containing the RSV LTR promoter without CTSs (data not shown) was utilized as a control (C). The reporters were cotransfected in COS-6 cells along with the expression vectors for the wt and mutant CTCF forms, as indicated at each bar of each panel. The reporter activity was measured as described in Materials and Methods. The CAT values were normalized to the total cell extract protein concentration and were expressed in relative units by taking the activity of pPst2myc-CAT cotransfected with the empty expression vector pSG5 at an input of 1.0 μg per plate as 1.0 U. The results shown represent the mean values with the standard deviations obtained in the cotransfection experiments repeated two times in triplicate plates for each combination of the reporter and effector plasmids. (D) Accumulation of the wt and mutant chicken CTCF proteins produced in COS-6 cells from transiently transfected expression vectors for CTCF without myc tags as described in Materials and Methods. con., control. Numbers in parentheses indicate the amount of effector vectors (in micrograms) used for each transfection.