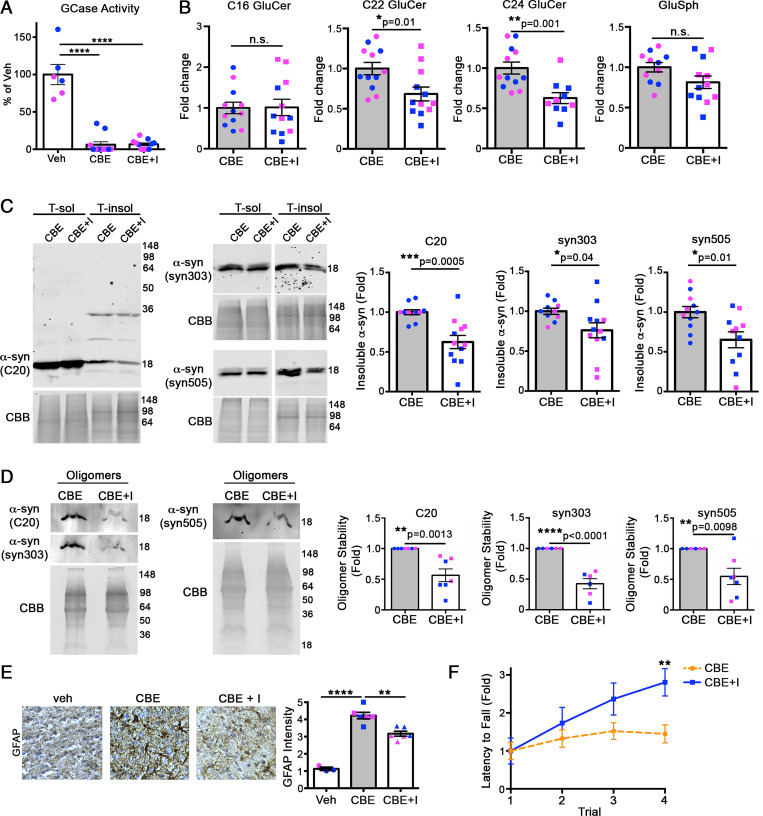
Fig. 4.
Reduction of long-chain GluCers rescues α-syn pathology in CBE-injected mice. The 3-mo-old wt mice were sequentially treated with CBE alone for 7 d, followed by CBE and venglustat, a glucosylceramide synthase inhibitor (I), for an additional 7 d. Cortex was then harvested and analyzed. (A) GCase activity was measured in cortical lysates, normalized to total protein, and expressed relative to vehicle (veh) control (n = 12 per group). (B) GluCers and GluSph from cortex were quantified by supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC)-mass spectrometry (MS)/MS analysis and normalized to inorganic phosphate (Pi) (n = 12 per group). (C) Cortex was sequentially extracted and separated into triton X-100 soluble (T-sol) and insoluble (T-insol) fractions followed by Western blot for α-syn. GAPDH and Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) were used as loading controls. Quantifications are shown on the right. (D) Quantification of pathogenic α-syn oligomers by SEC/Western blot. T-sol lysates were treated with 0.1% SDS to reveal stable, pathogenic oligomers followed by SEC analysis, quantified to the right (n = 6 to 7). C20 (rabbit pAb) and syn303 (mouse mAb) were sequentially probed on the same blot and detected with distinct, fluorescent secondary antibodies. Syn505 is shown on a separate blot. (E) Immunohistochemical analysis of cortical regions of treated mice reveals a reduction in GFAP staining, suggesting reduced neural injury at day 14 post-injection. Values are the mean ± SEM, Student’s t test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. Each plot shown represents an individual mouse (pink, female; blue, male). (F) Rotarod performance was tested at day 14 in mice injected with either CBE alone or CBE + venglustat (n = 4). Values are the mean ± SEM; Student’s t test was used for B–D, and F; ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test was used for A and E; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. N.S., not significant.