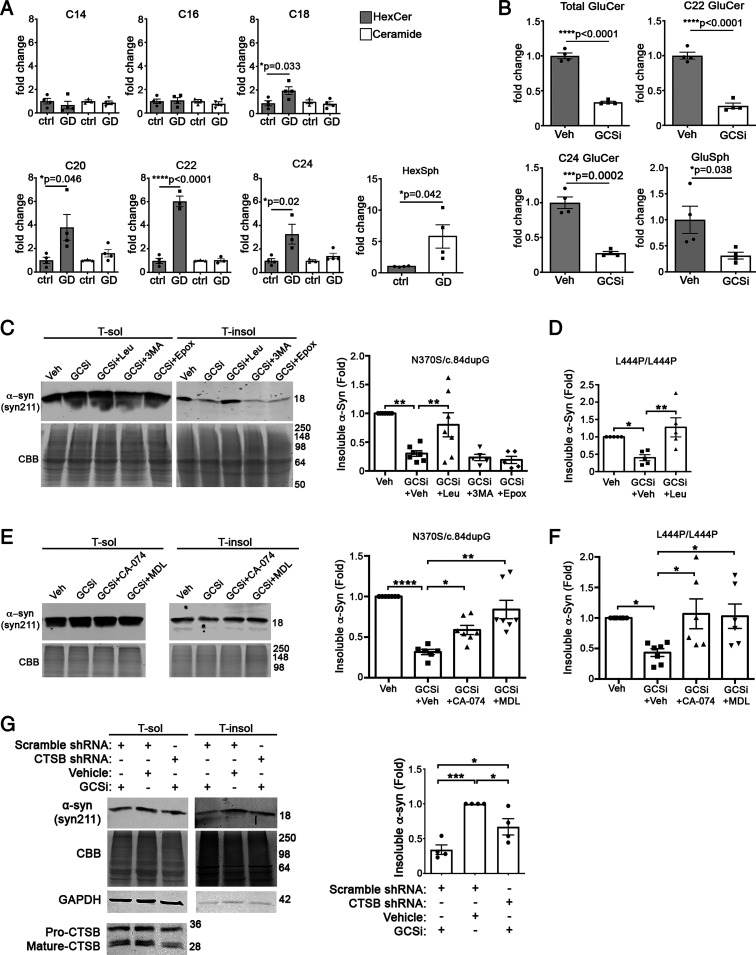
Fig. 6.
Long-chain GluCers selectively accumulate in nGD patient midbrain cultures, and their reduction lowers α-syn in a cathepsin-dependent manner. (A) Lipidomic analysis reveals accumulation of long-chain GluCers in GD neurons expressing N370S/c.dup84GG (n = 3 to 4 culture wells). (B) Treatment of GD midbrain cultures with 50 nM venglustat (GCSi) reduces long-chain GluCers and GluSph. (C) iPSCs from nGD patients were treated with venglustat and proteolytic inhibitors, and then analyzed at day 75. Sequential extraction/Western blot of iPSC–midbrain cultures from GD patients expressing N370S/c.84dupG mutations were treated with GCSi and inhibitors of lysosomal cathepsins (Leupeptin, Leu), macroautophagy (3-MA), or the proteasome (Epox). (D) iPSC–midbrain cultures from nGD patients expressing L444P/L444P mutations were analyzed as in C. (E) GD neurons expressing N370S/c.84dupG mutations were treated with GCSi and specific inhibitors of lysosomal cathepsins, including CA-074Me (cathepsin B + L) and MDL 28170 (cathepsin B and calpain). (F) nGD neurons expressing L444P/L444P were analyzed as in E. (G) GD midbrain neurons expressing N370S/c.84dupG mutations were treated with lentiviral shRNA particles to knock down CTSB and then 2 d later were treated with 50 nM venglustat for 14 d. Cultures were analyzed as in C. Values are the mean ± SEM; unpaired Student’s t test was used for A and B; ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test was used for C–G; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.