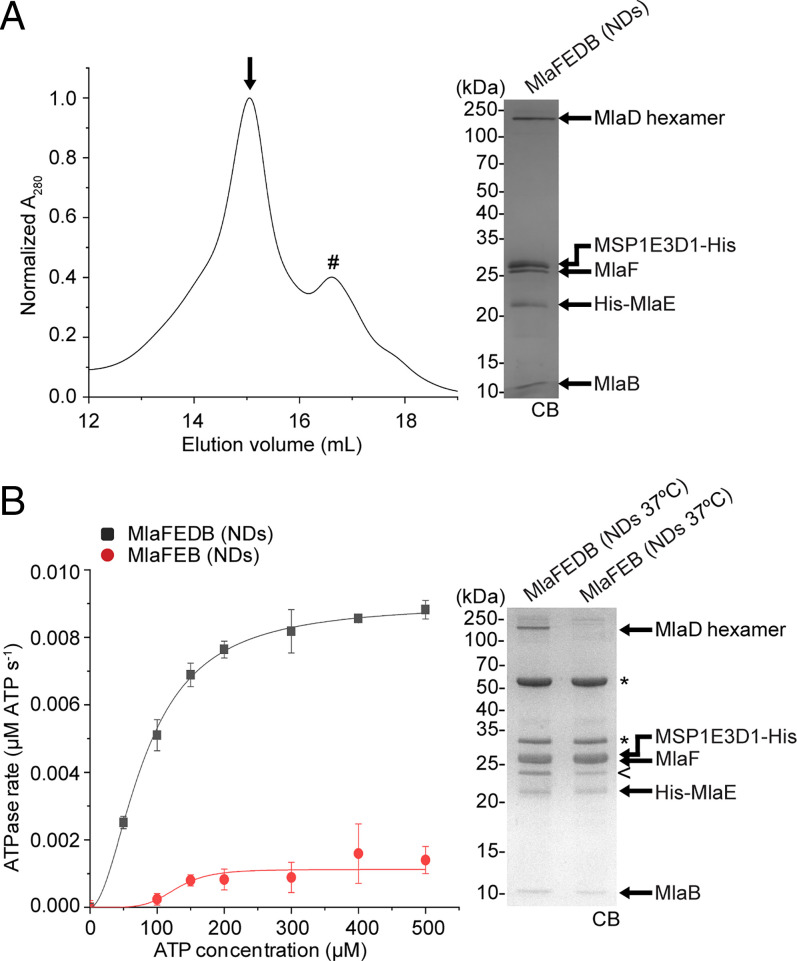
Fig. 1.
Nanodisc-embedded MlaFEDB exhibits higher ATP hydrolytic activity than MlaFEB. (A) Size-exclusion chromatographic profile of nanodisc-reconstituted (NDs) MlaFEDB complex. SDS-PAGE analysis of the peak fraction (annotated with an arrow [↓]) is shown on the Right. #, empty NDs. (B) Enzyme-coupled ATPase assays of nanodisc-embedded MlaFEDB and MlaFEB complexes (0.1 μM) at 37 °C. Average ATP hydrolysis rates from triplicate experiments were plotted against ATP concentrations and fitted to an expanded Michaelis–Menten equation that includes a term for Hill coefficient (n); MlaFEDB NDs (kcat = Vmax/[complex] = 0.090 ± 0.002 μmol ATP s−1/μmol complex, Km = 82.5 ± 4.3 μM, n = 1.9 ± 0.2) and MlaFEB NDs (kcat = 0.011 ± 0.002 μmol ATP s−1/μmol complex, Km = 129.1 ± 12.8 μM, n = 5.3 ± 2.0). Errors depicted by bars and ± signs are SDs of triplicate data. SDS-PAGE analysis of the complexes used for these assays is shown on the Right. *, pyruvate kinase/lactate dehydrogenase enzymes used in coupled assay; <, degraded MSP1E3D1. CB, Coomassie blue staining.