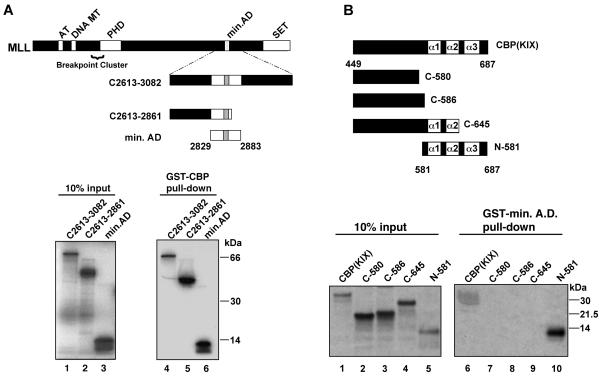
FIG. 2.
In vitro binding assays define minimal interaction domains of MLL and CBP. (A) GST-CBP (encompassing murine CBP amino acids 449 to 687) was tested for interaction with the indicated MLL polypeptides. The diagram shows full-length MLL and the internal polypeptides used in this experiment; numbering is based on GenBank accession number NM005933 (57). 35S-labeled MLL polypeptides were generated by in vitro transcription and translation as described in Materials and Methods. In lanes 1 to 3, 10% of the input 35S-labeled protein was analyzed by SDS-PAGE in parallel with proteins remaining bound to the GST-CBP beads (lanes 4 to 6). Binding to GST was undetectable under these conditions (see Materials and Methods). (B) GST-MLL A.D. (amino acids 2829 to 2883) was tested for binding to the indicated CBP polypeptides. A series of PCR templates encoding portions of the murine CBP KIX domain were transcribed and translated as described in Materials and Methods. Input protein (lanes 1 to 5) was analyzed by SDS-PAGE in parallel with proteins remaining bound to the GST-MLL A.D. beads (lanes 6 to 10). Murine CBP numbering follows as described (8). All binding reactions were repeated in at least three independent experiments.